Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
N
N
H
2
O
R
′
O
RN
C O
R
′
O
RNH
2
+ CO
2
O
O
O
N
N
N
R
NH
O
R
RN
R
O
RNH
2
R
O
R
H
H
′
O
C O
+
′
′
R
′
O
O
O
O
Urea linkage
Another type of thermoset is the phenol formaldehyde resins, also known
as phenolic resins. They are the first truly synthetic polymer [38] to be devel-
oped and are often referred to as Bakelite after Leo Bakeland, who invented
them in 1907. Phenolic resins are made by reacting phenol with formalde-
hyde under acidic or basic conditions. Under basic conditions, a greater than
a 1:1 molar ratio of formaldehyde to phenol is used and the product is called
a resole. Under acidic conditions, less than a 1:1 molar ratio of formaldehyde
to phenol is used and the product is called a novolak [39]. Under basic condi-
tions, the reaction proceeds by an aldol condensation type mechanism to give
the hydroxymethylphenol. This in turn can react with another phenol to give
a methylene bridged bisphenol and then with more formaldehyde and phenol
to give the resole.
OH
H
O
−
O
O
−
O
O
OH
H
H
H
H
Base
Tautomerization
CH
2
OH
O
O
−
O
H
+
H H
H H
HO
CH
2
OH
OH
HO
OH
CH
2
OH
CH
2
OH
Base
H
H
OH
O
CH
2
OH
Resole
The resole is not specifically the compound shown, but rather a mixture of
that and similar structures. The resole can then be heated in a mold to give
further condensations and a thermoset polymer.
Under acidic conditions, phenol reacts with formaldehyde by an elec-
trophilic aromatic substitution mechanism. This in turn can react with
another phenol to give a methylene bridged bisphenol and then with more
formaldehyde and phenol to give the novolak. The novolak is not specifically
the compound shown, but rather a mixture of that and similar structures.







































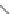
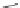









































Search WWH ::

Custom Search