Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
cyclopentadienyl, indenyl, or fluorenyl systems. Often, as in the above
example, the aromatic anionic ligands are bridged to each other.
Other systems may have one aromatic anionic ligand. These are not
strictly metallocene catalysts, but are more properly referred to as single-site
catalysts. They provide a single active site for the polymerization as opposed
to Ziegler - Natta systems which have many active sites. Because there is a
single active site, they tend to produce polyolefins with a narrower molecular
weight distribution. The molecular weight distribution has a strong influence
on certain properties such a viscosity versus shear and impact. One example
of a single site organometallic catalyst is the system developed by Dow
Chemical [12].
CH
3
H
3
C
H
3
C
Ti
Si
CH
3
N
Dow constrained geometry catalyst
Equistar researchers have developed systems based upon heterocyclic
pi-anionic ligands such as indenylindolyl [13] or boratabenzene derivatives
[14].
H
3
C
N
Cl
Cl
Zr
CH
3
Cl
Cl
Zr
B
H
3
C
N
CH
3
The choice of the catalyst can influence many physical properties such
as toughness, processability, and heat capabilities. These properties are
determined by the molecular architecture, things such as molecular weight,
stereochemistry, comonomer incorporation, etcetera. The ability to change
the catalyst to make a modified polymer suitable for new applications is of
great commercial significance and ensures continued research in this area.
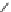
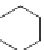
Another type of polymerization that also uses organometallic catalysts is
ring-opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP) [15 - 17]. This is not used
for the major volume polymers but is discussed here because it represents
another method of polymerization. The word, “metathesis” derives from








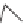





































Search WWH ::

Custom Search