Java Reference
In-Depth Information
<h:message for="lastName" />
<h:outputLabel for="age" value="Age:"/>
<h:inputText id="age" label="Age" size="2"
value="#{registrationBean.age}"/>
<h:message for="age"/>
<h:outputLabel value="Email Address:" for="email"/>
<h:inputText id="email" label="Email Address"
required="true"
value="#{registrationBean.email}">
</h:inputText>
<h:message for="email" />
<h:panelGroup/>
<h:commandButton id="register" value="Register"
action="confirmation" />
</h:panelGrid>
</h:form>
</h:body>
</html>
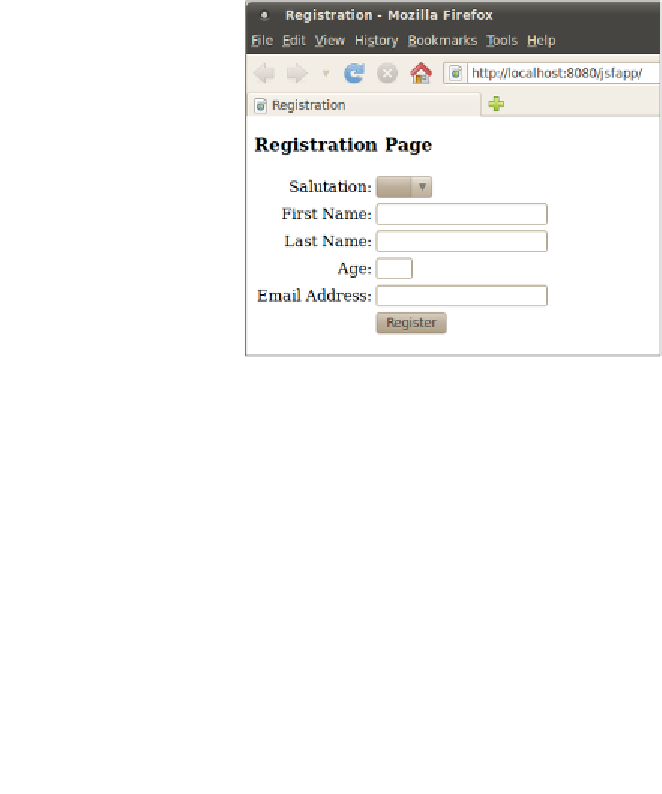
The following screenshot illustrates how our page will be rendered at runtime:
All JSF input fields must be inside an
<h:form>
tag. The
<h:panelGrid>
helps us
to easily lay out JSF tags on our page. It can be thought of as a grid where other JSF
tags will be placed. The
columns
attribute of the
<h:panelGrid>
tag indicates how
many columns the grid will have, each JSF component inside the
<h:panelGrid>
component will be placed in an individual cell of the grid. When the number of
components matching the value of the
columns
attribute (three in our example) has
been placed inside
<h:panelGrid>
, a new row is automatically started.