Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
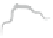
Fig. 2.11
Rule of polygon
applied to the forces
F
1
,
F
2
,
and
F
3
to obtain the
resultant
R
. The polar rays
which connect the point
P
to
the head of each vector were
drawn in sequence
F
1
F
2
F
3
F
2
F
1
R
F
3
B
C
A
D
P
2.4.2 Resultant of Two or More Nonparallel Forces Applied
on a Body and Its Line of Action: Method of Funicular
Polygon
To find graphically the line of action of the resultant of two or more coplanar forces
applied on a body, we construct the funicular polygon. Consider the forces
F
1
,
F
2
,and
F
3
in Fig.
2.11
. We want to find the magnitude of the resultant
R
and its line of action.
The magnitude and the direction of the resultant
R
can be obtained by the rule of
polygon. To use this method, we only need to draw straight lines parallel to the lines of
action of these forces, which can be done with the help of two squares. The first step
consists in the transportation of the vectors to add them by the rule of polygon, as
shown in Fig.
2.11
. After drawing the resultant, we adopt a point
P
and connect it with
straight lines A, B, C, and D, called polar rays, to the vertices of the polygon.
After that, we transport these polar rays, using the same direction as the original
situation. For this, the straight line A is drawn in a way to intercept the line of action
of vector
F
1
at any point. From this point of intersection, we draw the line B until it
cuts the line of action of
F
2
. From this intersection, we draw line C until it meets the
line of action of
F
3
. Finally, from this point, we draw line D. At the intersection of
lines A and D, the line of action of the resultant
R
should pass and, furthermore,
should be parallel to the vector
R
, obtained by the rule of parallelogram (Fig.
2.11
).
We have to be careful to draw always parallel lines, when transporting vectors, and
polar rays from one figure to another. Note that sometimes the line of action of the
resultant can pass outside the object subjected to the forces. The resultant of three
forces applied on a body by the method of funicular polygon is shown in Fig.
2.12
.