Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
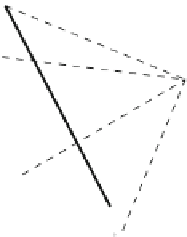
Fig. 2.12
Construction of
funicular polygon to
determine the line of action
of the resultant of the three
coplanar forces
A
B
F
1
C
D
R
F
2
F
3
Once the magnitude and direction of the resultant force and its line of action
have been determined, the torque due to this resultant can be calculated about any
axis of rotation. This can be done after obtaining the arm
d
⊥
and using (
2.1
) and
specifying the direction of rotation.
Example 2.2
Consider a bar of 38 cm in length subjected to three coplanar forces
with magnitude
F
1
¼
11.8 N, as illustrated in the
figure of Example 2.2. Determine the resultant force vector by the method of
polygon and then apply the method of funicular polygon to obtain the line of action
of the resultant force. Then, find the torque of the resultant force about the axis of
rotation through O.
5.1 N,
F
2
¼
12.6 N, and
F
3
¼
F
3
F
1
F
2
A
F
1
B
P
C
D
F
2
R
F
3