Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
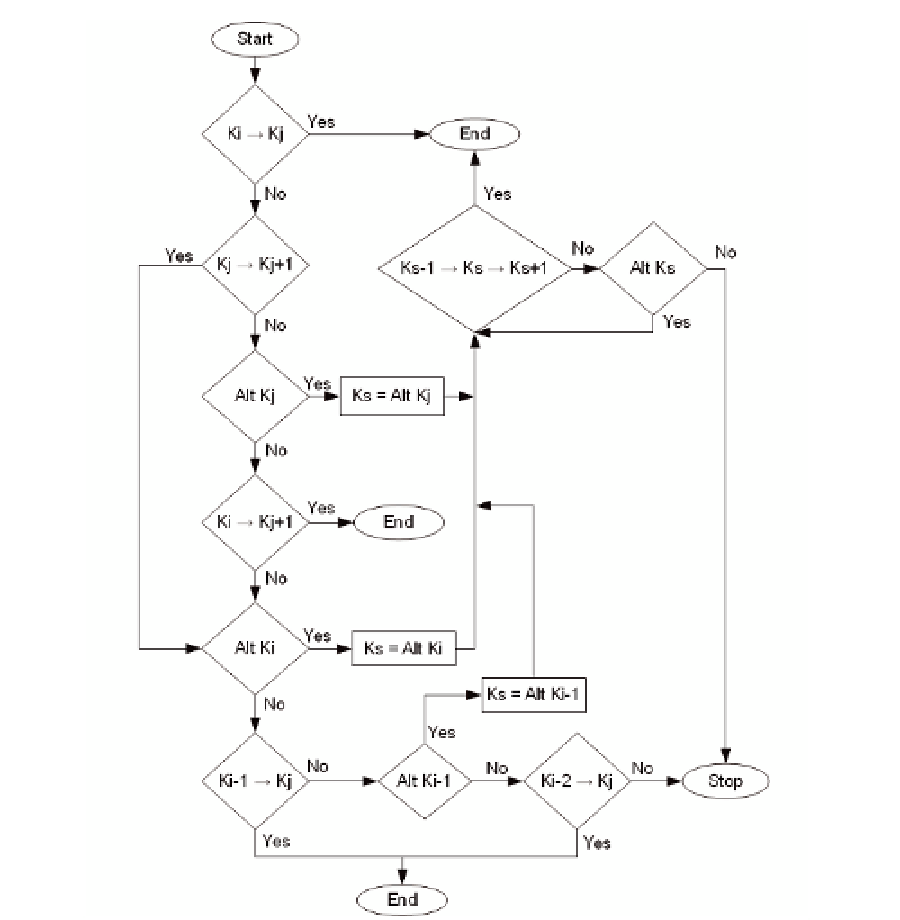
Fig. 5. Flow Diagram with the Step Sequence of the Map-Matching Algorithm
3.2 Example of an implementation of the algorithm
The example illustrated in Figure 6 includes a set of Differential GPS (DGPS) data points
collected every five seconds by a winter maintenance vehicle during the 2002-2003 winter
season in Columbia County, Wisconsin. The spatial mismatch, occurring at the diverging
roadways in this figure, is resolved by implementing the decision-rule map-matching
algorithm. Points 0, 2, 3, and 4 are snapped to the nearest roadway within their 35-foot
buffers, resulting in points S0, S2, S3, and S4 (shown as rectangles). Points S0, S3, and S4 are
on the Interstate 39 centerline, while point S2 is situated on the ramp centerline. Note that no
roadways are contained within the buffer for GPS data point 1, thus, this point is not used in
determining the feasible path.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search