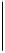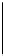Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
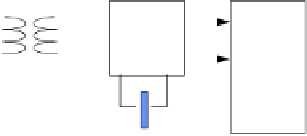
reset
Comp
u
ter
clock
Recovered
clock from
network
Control logic
Interface
signal
CLK
Reset
Reset
FF
EF
Write
Read
SIPO
(serial-in
parallel-out)
FIFO
(first-in
first-out)
Data
out
Data in
Figure 26.21
Memory buffering
AM7204A
(FIFO)
SEEQ 8020
(PLL)
74164
(SIPO)
RX+
RXI
Data
QA
D0
Q0
RX+
RxD
A
SEEQ
83C92A
RX-
RX-
CLK
RxC
CLK
QH
D7
Q7
X1
X2
GND
-9V
W
R
20 MHz
NMA
0509S
(5V to - 9V
convertor)
GND
5V
Figure 26.22
Ethernet receiver
26.13 Gigabit Ethernet
The IEEE 802.3 working group initiated the 802.3z gigabit Ethernet task force to create the
gigabit Ethernet standard (which was finally defined in 1998). The Gigabit Ethernet Alliance
(GEA) was founded in May 1996 and promotes gigabit Ethernet collaboration between or-
ganisations. Companies, which were initially involved in the GEA include: 3Com, Bay Net-
works, Cisco Systems, Compaq, Intel, LSI Logic, Sun and VLSI.
The amount of available bandwidth for a single segment is massive. For example, almost
125 million characters (125 MB) can be sent in a single second. A large reference book with
over 1000 pages could be send over a network, 10 times in a single second. Compare it also
with a
150 kB/s).
Gigabit Ethernet operates almost 35 times faster than this drive. With network switches, this
bandwidth can be multiplied by a given factor, as they allow multiple simultaneous connec-
tions.
×
24, CD-ROM drive which transmits at a maximum rate of 3.6 MB/s (24
×