Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
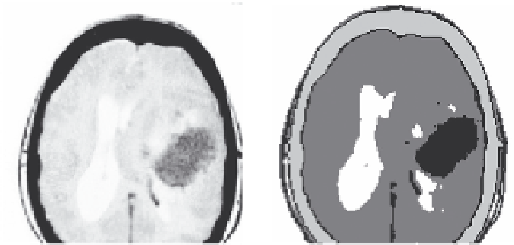
FIGURE 2.4
(a) Brain image 'tumour' and (b) intuitionistic fuzzy cluster.
to a group may contribute to different groups. So, the membership
values with respect to different groups are not 0. Intuitionistic fuzzy
clustering is also similar to fuzzy clustering; the only difference is
that the membership function is updated with the hesitation degree.
An example in Figure 2.4 shows fuzzy, intuitionistic fuzzy and
Type II fuzzy clustering.
4.
Edge detection
: Edges/boundaries of abnormal lesions/tumour or
any other abnormalities are required in image analysis. As medi-
cal images are poorly illuminated, the crisp decision as to whether
an edge is present in the image is very difficult. So initially edges
are sometimes enhanced before performing edge detection. The
fuzzy method may be very useful in alleviating such type of prob-
lem. There are many fuzzy edge detection techniques, but these
techniques may not find better edges in all the images. In that case,
intuitionistic fuzzy set and Type II fuzzy set may be useful where
more or different types of uncertainties are considered. An example
in Figure 2.5 shows fuzzy edges using interval-valued fuzzy set and
Type II fuzzy set.
(a)
(b)
(c)
FIGURE 2.5
(a) Knee patella image, (b) edge image using the interval-valued fuzzy set and (c) edge image
using the Type II fuzzy method.


Search WWH ::

Custom Search