Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
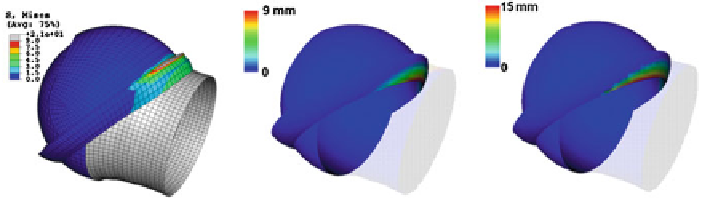
Fig. 8.5
Left
Von Mises stress in a deformed FEM model (
α
=60
◦
,CE=40
◦
).
Center
and
Right
Labrum is colored based on its radial and curvilinear penetration depths in the same model, respec-
tively (femur bone is semi-transparent) [
13
,
15
]; (
Left image
courtesy of Salman Chegini, ARTORG,
University of Bern) (With kind permission from Wiley: Journal of Orthopaedic Research, Pene-
tration depth method—novel real-time strategy for evaluating femoroacetabular impingement, Vol.
28, 2010, pp. 880-886, Arbabi E, Chegini S, Boulic R, Tannast M, Ferguson S J, Thalmann D,
Figs. 3 and 6)
For each hip model, a curve describing the maximum curvilinear and radial
penetration depths for different motion angles was created. For quantitative eval-
uation, the maximum of the curve values (peak) was extracted from each curve. In
order to detect patterns for the curvilinear and the radial penetration for specific hip
pathomorphologies, the difference of the normalized maximum penetration depths
was calculated. The calculated differences could show which type of penetration is
stronger for the corresponding hip pathologies (if the difference is positive (negative),
the curvilinear (radial) penetration depth is stronger).
8.3.4 Evaluation
Although the maximum penetration depth and maximum stress are not occurring in
the same zone (Fig.
8.5
.), there is a cause and effect relationship between them that
can be well quantified. Hence, the quantitative values resulting from the proposed
method were shown to be correlated strongly with the von Mises stresses of the
FE analysis [
15
,
23
]. The maximum curvilinear penetration depth was found for
a combined cam-pincer pathomorphology. The maximum radial penetration depth
was found for pure cam deformities. The maximum normalized difference between
curvilinear and radial penetration depths was found for combined cam-pincer hips.
The minimum normalized distance was seen for pure cam impingement. Finally
it could be concluded that the penetration depth method allows a differentiation
between characteristic pathomorphotypes related to femoroacetabular impingement,
and it can be used for real time medical applications, which are desired by physicians.