Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
system, as these could otherwise potentially contaminate or interfere with the
normal functions of the system; and robust and specific functional groups on
the surface to recognize and capture desire targets effectively.
6.4.4.2 Characterization of the Synthesis Process
Templating Study by AFM
Since the formation of mesoporous silica is built on the templates of surfactant
molecular suprastructure, studies on the interactions of micelles with silica
wafer which is used to represent the silica-coated surface on magnetic particles,
were performed first.
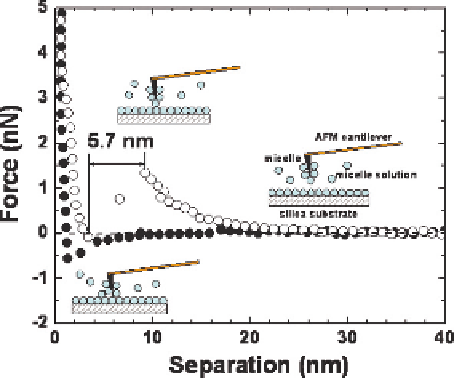
Figure 6.8 (solid squares) shows the interaction forces between a cantilever
tip and bare silica wafer in pure ethanol. There is a measurable attraction
between the two at the separation distance below 10 nm. This attractive force
is attributed to van der Waals forces. After replacing the ethanol by 5 mmol/L
CTAC (cetyl-trimethyl-ammonium chloride) in ethanol solution and incuba-
tion for 1 h, a repulsive force between the tip and the sample starting at 20 nm
during approaching is evident, as shown in Fig. 6.8 by open squares. This long-
range repulsion is attributed to overlap of electric double layers around two
positively charged surfaces. It appears that the cationic CTAC surfactant
adsorbs on both AFM tip and silica surfaces, rending them both positively
charged. At a separation distance around 9 nm, a maximum repulsive force
barrier is observed and the tip jumps inward by a distance of 5.7 nm. After this
jump-in, a continuous increase in repulsive force is observed as the sample
pushed upward against the AFM tip by about 4 nm. This type of force profiles
over such a short separation distance suggests a surface of compressible nature,
Fig. 6.8 Interaction forces between a bare silica wafer and AFM tip in ethanol (solid squares)
and CTAC ethanol solutions (open squares)