Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Case 2
Suppose a driver rents a camper for a long vacation. With a different
width, weight, and engine, the camper will require another driving
style. On the first day, driving the camper is so new that the conscious
system is very alert and helps to adjust the existing driving patterns.
After a few days, the camper starts to feel familiar and the driver
might easily fall back on his previous experience and automated beha-
viors. The safety intuition acts as if the driver is running his car, not a
camper. Experience is not yet gathered; the database is still empty.
Accidents can happen more easily in this period.
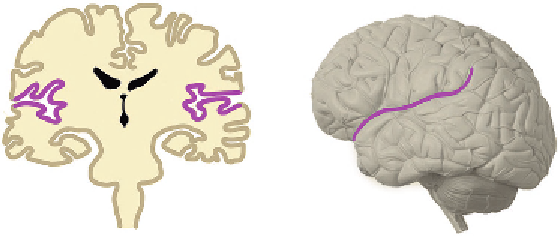
5.8 WHERE IN THE BRAIN?
From the outside, the cortex looks as if it is folded, which is actually
the case. It is full of curves. These are formed to increase the surface of
the modern brain. The top parts are called gyri; the deep parts, sulci.
On both sides of the cortex, we can see a temporal cortex, which looks
like an integral part but actually hangs there like an ear warmer. The
deep sulcus between the parietal cortex and the temporal cortex is
called the insula, sometimes referred to as the hidden cortex because
you cannot see it from the outside. It has many functions like the
analysis of sounds and the integration of all stimuli (smell, taste, and
touch) connected to eating food, and is important in the experience of
pain.
Parietal
cortex
Parietal
cortex
Frontal
cortex
Insula
Insula
Temporal
cortex
Temporal
cortex
The insula
The insula connects the more exterior modern brain with the more
interior emotional brain (Heuvel & Sporns, 2011). The insula scans all
sensory input and all our plans on both risk and on efficiency.
Inefficiency is treated in the same way as pain: Try to avoid it.