Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
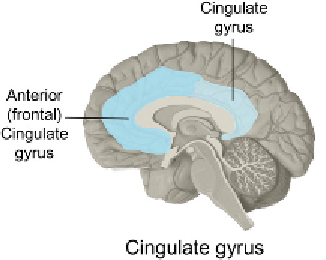
autobiographic memory. Several basic survival functions are stored here.
Alexander (2011) claims that this area not only focuses on risk and safety
problems in particular but on the outcome of processes in general.
Attention is directed via this gyrus. It has a strong connection with the
stress axis (the activation system in case we experience stress, also called
the HPA, the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis). We can experience
this gyrus when we have the
a sudden insight that
something is going wrong, sometimes combined with a shiver through
the whole body. Messages from this system are handled with priority
in the brain. Once the stress axis is activated, the whole system becomes
prepared for a rapid reaction to a dangerous situation. The perceived
danger or threat can be so strong that any possible action is estimated as
being useless. In this case, the brain activity changes to a more primitive
“
“
oops
”
feeling
—
pattern in which old intuitive behaviors take over. These
are the moments during which we have doubts as to whether any action
could still counter the danger or whether the best remaining option is
to run. In this case, the brain activity changes to the basic brain (Mobbs,
2009), and this area inhibits the activity of the anterior cingulated gyrus
like a hostile takeover. In the worst-case scenario, not even running is
considered as an option and the person literally freezes his gestures.
He feels like sticking to the floor and cannot move anymore.
hard-wired
”
4.5 SUMMARY
Risk understanding is an autonomous and mostly nonconscious brain
process. It scans past and present situations, extrapolates developments
into the near future and checks personal plans. The quality of scanning
can never be higher than the level of understanding. So the more pro-
cesses are understood, the easier the brain can scan them and detect
possible dangers. Time, available data, attention, and comprehending