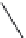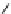Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
CH
3
O
(CH
3
)
2
N
= Z
CH
3
CH
2
CHO
N(CH
3
)
2
HO
O
Forosamine
R
2
O
O
O
CH
3
O
CH
3
OH
H
Mycaminose
H
O
1
CH
3
H
OR
3
CH
3
O
H
O
CH
3
O
Mycarose
R
3
R
1
R
2
Spiramycin I
H
Z
H
Spiramycin II
COCH
3
Z
H
Spiramycin III
COCH
2
CH
3
Z
H
Leucomycin A
1
H
H
COCH
2
CH(CH
3
)
2
CH
3
CH
3
H
N
R
1
C
R
2
C
3
H
7
CO
NH
C
H
HO
O
H
H
H
H
HO
OH
H
S CH
3
Lincomycin R
2
= H
R
1
= H
R
1
= OH
Clindamycin R
2
= Cl
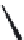
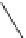
FIGURE 25.17
Macrolides and lincomycin (derivatives).
(
N
-acetylglycosamine units). The carboxyl group of NAM is linked to a short peptide, which forms
the bridge with another NAG-NAM strand.
One of the important new targets to develop antibiotics is the transglycosylase reaction, respon-
sible for the polymerization of the disaccharide units. During the transglycosylase reaction, the
coni guration of C
1
is changed from a to b. Moenomycin A, active against Gram-positive bacteria,
is a transglycosylase inhibitor (Figure 25.18).
The formation of the linkage between two peptide ends is catalyzed by a transpeptidase bound
to the outside of the cytoplasmic membrane.
This reaction regulates the degree of peptidoglycan cross-linking. In
Staphylococcus aureus
,
90% of the peptide chains are involved in cross-links, whereas in Gram-positive and Gram-negative
bacilli only 20%-50% of the strands are cross-linked.
Vancomycin kills bacteria by targeting lipid II. Lipid II is the target of several other classes of
natural products like lantibiotics, ramoplanin, and mannopeptimycins. Nisin that acts through a
lipid-II-dependent targeted pore formation mechanism is an example of a lantibiotic. Vancomycin
and teicoplanin dissociate with the acyl-d-Ala-d-Ala terminus of the growing peptidoglycan chain.
Both compounds are active against Gram-positive bacteria. Resistance against vancomycin is
observed when the d-Ala-d-Ala terminus is changed to d-Ala-d-Lac. Nisin is active against vanco-
mycin resistant bacteria because it does not interact with the amino acids of the pentapeptide chain
(Figure 25.19).