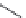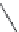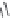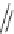Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
TABLE 25.7
Cephalosporins
O
S
R
1
C
NH
N
R
2
O
COOH
R
3
R
2
CH
2
OC
3
CH
NH
2
Cefaloglycin
O
CH
NH
2
CH
3
Cefalexin
CH
NH
2
CH
3
Cefradine
HO
CH
CH
3
Cefadroxil
NH
2
N
HO
CH
NH
2
CH
2
S
N
Cefatrizine
H
N
C
N
CH
2
CH
Cei xime
H
2
N
S
OCH
2
COOH
CH
NH
2
Cl
Cefaclor
The blood concentrations obtained after oral administration of the above described cepha-
losporins are low. Cefaloglycin, the i rst cephalosporin that gave moderate blood levels after oral
administration, has a phenylglycine side chain. This group or a related group is present in several
oral cephalosporins. Cefalexin, which is the most widely used product, has an activity that is much
lower than that of the injectable compounds. Attempts to increase the activity have not been very
successful, but cefaclor and cei xime are somewhat superior (Table 25.7).
25.2.1.4 Nontraditional
b
-Lactam Antibiotics
25.2.1.4.1 Clavulanic Acid and Sulbactam
Clavulanic acid discovered in the Beecham laboratories in 1976 is a b-lactam produced by the
same Actinomycete
Streptomyces clavuligerus
that produces cephamycin C. Its
in vitro
activity is
low, but it is a potent inhibitor of many b-lactamases. It is combined with conventional b-lactams
like amoxicillin and ticarcillin. It potentiates the actions of these antibiotics against b-lactamase