Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
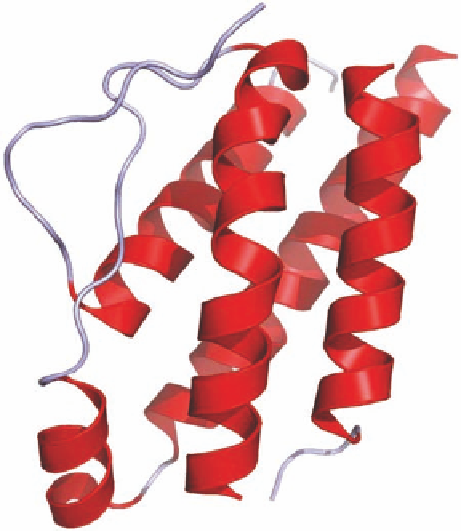
FIGURE 22.10
IL-2 is a soluble protein of 133 amino acids. It is characterized by four α-helixes that are
bundled together and belong to the structural family of cytokines called the four α-helix bundle family.
Other interleukins in this subfamily are IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-7, IL-9, IL-11, IL-12, IL-13, IL-15, IL-21,
and IL-23.
Basiliximab (Simulect
®
) is a chimeric (70% human and 30% murine) mAb utilized in the
prevention of acute organ rejection. This mAb has specii city and high afi nity for the subunit
of the IL-2 receptor (IL-2Ra, also known as CD25 or Tac) preventing IL-2 from binding to the
receptor on the surface of activated T cells. By acting as an IL-2 antagonist, basiliximab inhibits
IL-2-mediated activation and proliferation of T cells, the critical step in the cascade of cellular
immune response of allograft rejection. Therefore, basiliximab has a long half-life of ~7-12 days
and saturates the IL-2 receptor for up to 59 days. Other ILs or IL receptor antagonists in clinical
development are IL-6, IL-10, IL-12/23, IL-15, IL 20, and IL-21.
22.5.4 B C
ELL
D
EPLETION
As a therapy for cancer, mAbs can be injected into patients to seek out the cancer cells, potentially
leading to disruption of cancer cell activities or to enhancement of the immune response against the
cancer. This strategy has been of great interest since the original invention of mAbs in the 1970s.
After many years of clinical testing, researchers have proven that improved mAbs can be used
effectively to help treat certain cancers. An antibody called rituximab (Rituxan
®
) can be useful in
the treatment of leukemias and other new mAbs are undergoing active testing.
Rituximab is a chimeric mAbs directed against the CD20 antigen specii c to B-lymphocytes.
Once the antibody recognizes the surface antigen, the Fc part of the antibody recognizes Fc recep-
tors on the NK cells and induces ADCC. It has been used for a number of years in the treatment of
B cell lymphomas. Various data now suggest an important role for B-lymphocytes in the inl am-
matory cascade of RA that causes the destruction of cartilage and erosion of bone. Rituximab may
intervene by destroying the B cells that produce auto antigens (rheumatoid factor). Systemic lupus
erythematosus (SLE) is a disease that is driven by B cells that produce antibodies directed against