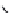Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
OH
α
1
β
2
γ
2S
expressed
in
Xenopus
oocytes
ρ
1
-HEK293 cell
line
R
5
O
EC
50
(μM)
EC
50
(μM)
N
HN
(+)-CAMP (
15.30
)
>1000
39.7
IAA (
15.28
)
310
13
R
2
5-Me-IAA (
15.40
)
5-Ph-IAA (
15.41
)
>1000
22
R
2
, R
5
= H (IAA (
15.28
))
R
2
= H, R
5
= Me (5-Me-IAA (
15.40
))
R
2
= H, R
5
= Ph (5-Ph-IAA (
15.41
))
R
2
= Me, R
5
= H (2-Me-IAA (
15.42
))
>1000
420
2-Me-IAA (
15.42
)
>1000
>1000
FIGURE 15.10
Functional data of IAA (
15.28
) and analogs (
15.40
,
15.41
, and
15.42
) from
Xenopus
oocytes
expressing
α
1
β
2
γ
2
receptors using two-electrode voltage-clamp recordings or a h
ρ
1
-HEK293 cell line in the
FLIPR membrane potential assay.
GABA
A
GABA
C
α
1
Arg119
Arg158
β
2
Tyr205
Tyr247
α
1
Arg66
Arg104
β
2
Tyr157
Tyr198
Ser168
α
1
Thr129
β
2
Tyr97
Phe138
(A)
(B)
FIGURE 15.11
GABA and 5-Me-IAA (
15.40
) docked into the orthosteric sites of models of (A) the GABA
A
receptor and (B) the GABA
C
receptor. The ligands GABA and 5-Me-IAA are shown using orange and green
carbon atoms, respectively. Hydrogen atoms other than those on the ligands are omitted for clarity. Proposed
hydrogen bond interactions are shown as dashed lines. (Adapted from Madsen et al.,
J. Med. Chem
., 50, 4147,
2007.)
15.6 GLUTAMATE—NEUROTRANSMITTER AND EXCITOTOXIN
Glu is ubiquitously distributed in high concentrations in the CNS and Glu serves other important
functions apart from being the major excitatory neurotransmitter, e.g., as building block in proteins
and precursor for the neurotransmitter GABA. A very important aspect of Glu functions is the
fact that high concentrations of Glu is neurotoxic, which led to the term excitotoxicity even before
Glu was recognized as a neurotransmitter. Excitotoxicity describes the ability of all Glu receptor
agonists to excite neurons and at the same time being neurotoxic, if the neurons are exposed to the
agonist for too long a period and/or exposed to a high concentration of the agonist.
15.6.1 R
ECEPTOR
C
LASSIFICATION
AND
U
PTAKE
M
ECHANISMS
The targets at the Glu receptor system are receptors, allosteric sites, uptake mechanisms, and Glu
metabolism (see Figure 15.1). However the primary focus has been on the ligands and their receptor