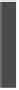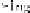Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
a)
b)
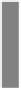
Figure 6.13
Comparison of the mean extension between 5 stroke and 5 elderly subjects
during hand opening (extension). (a) Showing the maximum extension achieved in all
cycles. Best result is 100% equals full extension. (b) Showing the maximum flexion achieved
in all cycles. Best result is 0% equals complete hand grasp position. The vertical bar is
the standard deviation and the shaded bar is the mean average. For color reference, see
page 216.
Figure 6.13
shows the comparison of the maximum range between the elderly
and stroke subjects. For hand opening task, the healthy elderly group covered
almost the full range of extension whereas the stroke subjects had difficulty in
extending their fingers. And for hand grasp task, the elderly had better muscle
control than the stroke subjects to achieve more flexed position.
6.5 CONCLUSION
Rehabilitation of the distal motor functions of the upper extremity has been a
challengeforthetherapistsforalongtimeandtherecoveryofhandfunctions
is important to the stroke patients and elderly for their daily activities. With the
new hand rehabilitation robot, stroke patients can actively train their hand opening
and closing functions using their own EMG signals and learn. Learn to use their
voluntary EMG signals to control the hand motion. Although stroke subjects had
weak muscle strength and control, they demonstrated a better range of motion
achieved during training with the assistance from the hand rehabilitation system.
Further training with longer training period and greater intensity may be required