Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Box 22.3
Typical examples of groundwater-surface water (GW-SW) interaction in lowland basins
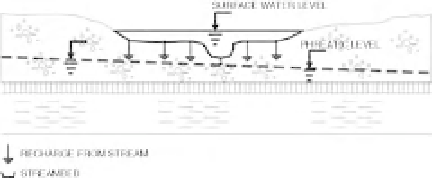
Recharge from leaky streams to an aquifer.
Note variation of streambed thickness
between the main channel and the
floodplain.
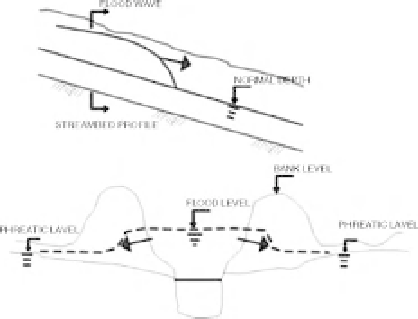
Bank storage attenuation effects when a
flood wave passes along a stream.
Seasonal water level fluctuations beneath
the floodplain of a river, driving changes
in wetland hydrology and diversification
of habitats, especially at water margins.
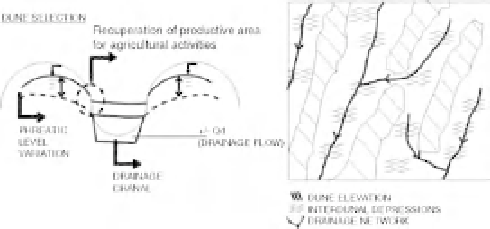
Coupling between surface water,
groundwater processes and artificial
drainage channels is a key factor that
determines flow to drains and efficiency
of the drains in terms of water table
drawdown. This must be understood and
accounted for in the engineering design
and operational rules for artificial
drainage systems.