Game Development Reference
In-Depth Information
In some technology trees, players can research each technology only once; however,
many technologies require the player to have researched one or more technologies
before. For example,
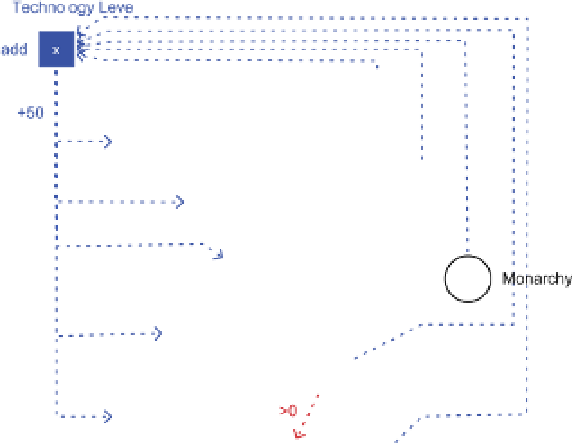
Figure 6.53
represents a technology tree that is not unlike the
one found in
Civilization
. Keep in mind that the effect of having a particular tech-
nology is omitted from this diagram. However, it is easy to imagine that technologies
such as the alphabet and writing increase the resources available for research. In
this diagram, the red connections enforce the order in which technologies must
be researched, while the blue construction keeps track of the number of resources
developed and adjusts the research prices accordingly.
FIGURe 6.53
a
Civilization
-style
technology tree
In this chapter, we introduced a few additional features of the Machinations
Tool and then took a much closer look at two important mechanics design tools:
feedback loops and randomness. We explained seven different characteristics of
feedback: type, effect, investment, return, speed, range, and durability. Each of these
has a distinct effect on the behavior of an internal economy.
In the section “Randomness vs. Emergence,” we showed how you can use random-
ness to create unique situations that force players to improvise. We also explained
that randomness can help prevent dominant strategies: Because randomness
changes a game's state unpredictably, you are less likely to create a game in which
one strategy is always the best one.
We ended the chapter with an extensive discussion of ways to use Machinations
diagrams to model economic structures in traditional genres of video games.