Databases Reference
In-Depth Information
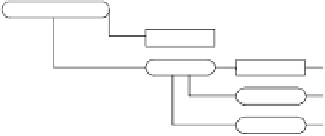
account_operation
bankAccN
“0012”
id
opertion
“00025”
account_operation
type
amount
bank transfer
id
“00025”
$ 1,500
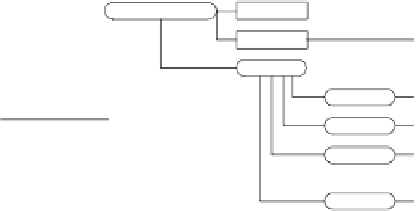
request
number
date
“10”
recipient
0023
04-20-2007
Invoice 315 of
03-31-2007
notes
means
Internet
(a) Alice's view
(b) David's view
Fig. 4.
Examples of views
4.2 Kudo et al. Static Analysis
Most of the access control systems proposed for XML documents are based on
a run-time policy evaluation, that is, any time an access request is submitted
to the system, the access control policies are evaluated. However, this run-
time policy evaluation may be quite expensive [13]. To avoid this problem,
Kudo et al. proposed an access control system based on
static analysis
,which
is complemented by a run-time analysis when needed [13].
Authorization Specification
Access authorizations are defined as triples of the form (
s,
a, o
), stating that
authorization subject
s
is (or not, depending on the sign) allowed to perform
action
a
on object
o
.
An authorization subject may be a user-id, a role, or a group name: the
subject name is preceded by a prefix indicating its type. Note that hierarchical
structures are not supported by this model. The XPath language is used to
define objects in an authorization rule, but functions are not handled by the
considered model. Like in [9], the authors limit the basic model definition to
read authorizations only, and support both positive and negative authoriza-
tions to easily handle exceptions. However, this model does not distinguish
between schema and instance level authorizations.
Authorizations specified on an element can be defined as applicable to the
element's attributes only (
local
authorizations) or, in a recursive approach,
to its subelements and their attributes (
recursive
authorizations). To solve
conflicts that may arise on a node, the proposed model can adopt either the
“denials take precedence” or the “permissions take precedence” principles,
independently from the node on which the conflicting authorizations have been
specified. For security reasons, the model presented in the paper limits the
analysis to “denials take precedence” principle adoption. The default closed
policy is applied when no authorizations are specified.
±