Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
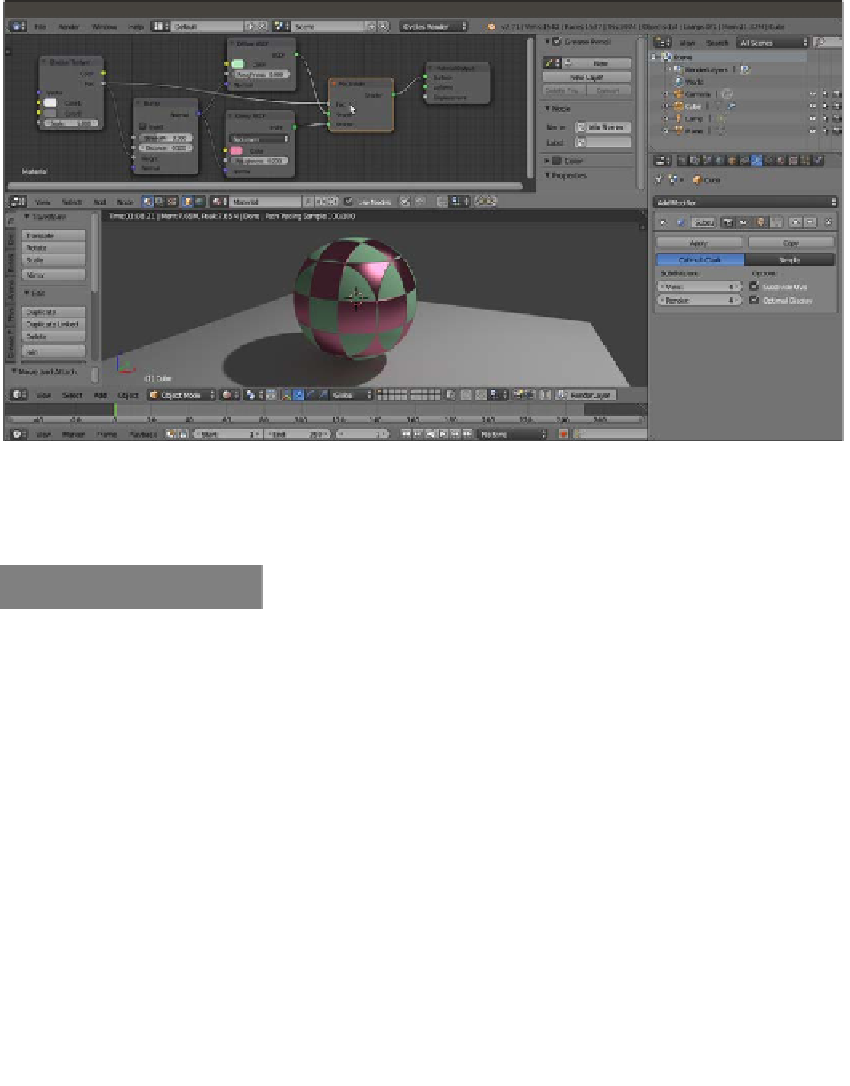
10. Connect the Fac output of the Checker Texture node to the Fac input socket of the
Mix Shader node and to the Height input socket of the Bump node, as shown in the
following screenshot:
The effect of a Checker Texture used as bump and especially as blending factor to mix the two components of the
material
11. Save the file as
start_03.blend
.
How it works...
From step 1 to 3, the changes are immediately visible in the Rendered viewport. At the moment,
the Wave Texture node color output is connected to the color input of the Diffuse BSDF shader
node, and the Spheroid looks as if it's painted in a series of black and white bands. Actually,
the black and white bands of the texture node override the green color of the diffuse
component of the shader, while keeping the material's pink glossy component unaltered.
In step 5, we did exactly the opposite. We disconnected the texture output from the Diffuse
shader to connect it to the Glossy shader color input. Now we have the diffuse greenish color
back and the pink has been overridden, while the reflection component is visible only inside
the white bands of the wave texture.
In step 6, in addition to the color output, every texture node also has a Fac (factor) output
socket, outputting gray-scale linear values. When connected to the Roughness input socket
of the Glossy shader, the texture output works as a factor for its reflectivity. The Spheroid
keeps its colors and gets the specular component only in the white areas on the surface
(that is, white bands represent total reflection and black bands represent no reflection).