Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
0.05
0.05
0.04
0.04
0.03
0.03
0.02
0.02
0.01
0.01
0
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900 1000
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900 1000
Training set size
Training set size
a
b
Linear Regression
Splines
0.05
0.01
0.04
0.008
0.03
0.006
0.02
0.004
0.01
0.002
0
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900 1000
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900 1000
Training set size
Training set size
c
d
Radial Basis Functions
Kriging
0.01
0.01
0.008
0.008
0.006
0.006
0.004
0.004
0.002
0.002
0
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900 1000
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900 1000
Training set size
Training set size
e
f
Evolutionary Design
Neural Networks
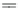
Fig. 8.11
Box plots of average normalized error versus training set size for logarithmic box-cox
transformation.
a
Linear regression,
b
Splines,
c
Radial basis functions,
d
Kriging,
e
Evolutionary
design,
f
Neural networks
for a specific use case depends on the desired accuracy and the constraints on the
prediction time. Referring to the use-case addressed in this section, however, we
discovered an exception to the previous
empiric
rule when, for
λ
=
0, Kriging gave
a better accuracy than Evolutionary Design for every training set size, paired with a
lower computation time.





























































































































































































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search