Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
regional vasoregulation
local vasoconstriction
1. wall stage
blood stasis
&
contact
PGD2
−
vWF
+
+
PAF
+
−
−
NO
TC plug
TC margination − aggregation
+
&
+
Ca
TC release (5HT, His, ADP, PGE2, PGF2a, TXA2, PGDF, ...)
PGE1
−
−
PGI2
TXA2
−
+
−
2. plasma stage
ATP
cAMP
intrinsec pathway
contact
extrinsic pathway
+
preKk
HMWK
III
−
+
XII
XIIa
+
VII
VIIa
+
XI
XIa
−
Kk
TFPI
α1AT
−
IX
IXa
−
TM−aPC−PS
−
VIII
VIIIa
−
Ca
X
Xa
AT3
−
−
V a
XIII
II
Tn
PS
PC
XIIIa
I
Fn
3. thrombodynamic stage
clot retraction
fibrinolysis
I
preKk
XIIa
HMWK
Png
Pn
chemotaxis
Kk
PAI
degradation products
UK
Bdk
C3a
fibrinopeptids
proUK
tPA
C3
−
α
2AP
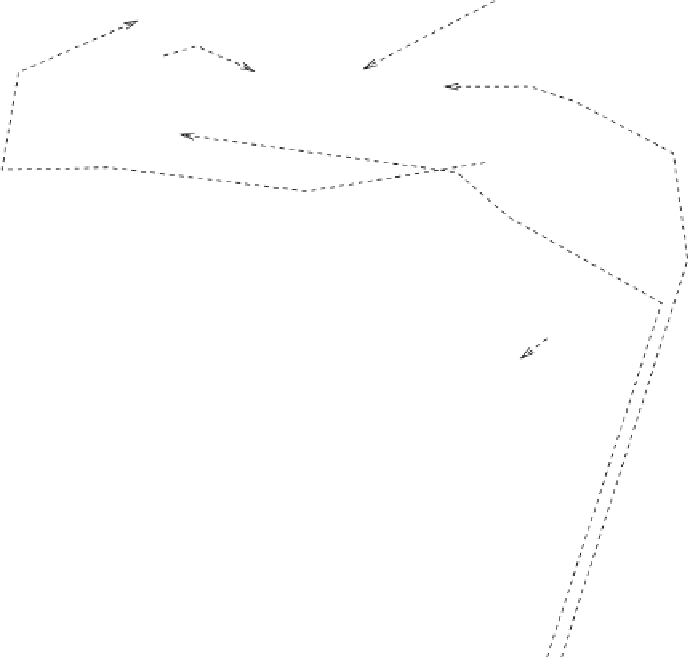
Fig. 9.6
Coagulation and fibrinolytic events. The contact-phase proteins include factors XII and
XI, prekallikrein, and high-molecular-weight kininogen (HMWK).
moduli for individual fibrin fibers in plasma clots assessed using optical tweezers are
1.7 (
±
±
3.5) MPa for unligated and ligated fibers, respectively [
1014
].
At large strains, clot stiffness increases. Strain-stiffening behavior prevents large
deformations that could threaten gel integrity. Theoretical networks of filamentous
proteins arranged in an open crosslinked mesh invariably stiffen at low strains
without requiring a specific architecture or different components with distinct
intrinsic stiffness [
1015
]. Some domains of fibrins unfold with stress. A blood clot
comprises platelets that control fibrin polymerization. Moreover, thrombocytes with
their actomyosin cytoskeleton generate large contractile stresses on fibrin clots.
1.3) and 14.5 (
























































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search