Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
electrode surface. The redox-labeled probe strand was replaced by
the complementary/noncomplementary target strands. The slower
rate of mismatched strands discriminated them from the fast
complementary sequences.
Kwon
et. al.
[102] introduced a signal on/off sensor based on
enzymatic cleavage of the unhybridized Fc-labeled ss-DNA resulting
inlowerelectrochemicalresponseforsinglemismatchedstrandand
no signal for non-complementary sequences. Another interesting
report by Panke
et. al.
[103]showstheelectrochemical assaybased
on competitive binding between the non-labeledtarget and the MB-
labeled reporter strand with a surface immobilized capture strand.
Sensitivity was reported up to 3 pmolar for nonlabeled binding
assay. Recent improvements include the use of locked-DNA (LNA),
[104] Scheme 7.4, and morpholino-oligomers, [105] to improve the
hybridizationa
nity.
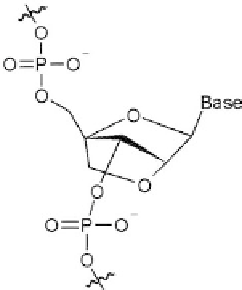
Scheme 7.4.
Exampleofalockednucleicacid(LNA)whichissignificantly
more rigid compared to conventional nucleic acids.
LNAs contain a methylene bridge that connects the 2'-oxygen
atom with the 4'-carbon atom of the ribose ring of the ribonucleic
acid resulting in a locked 3'-endo conformation, which reduces the
conformational flexibility of the ribose and increases the degree of
local organization of the phosphate backbone. Presumably entropic
constraint improves the ability of hybridization a
nity of the
capture strand. On the other hand, morpholino-oligomers are DNA
analogs in which the sugar phosphate backbone is replaced with