Graphics Programs Reference
In-Depth Information
noise texture is named “Tex.” Click on “Tex” and
switch to object mode; the vertices on the cube's
surface have been displaced according to the inten-
sity of the texture mapped to the surface of the cube
(Figure 12.60, left). You will have to play around
with the values in the “Modifiers” tab to establish
their effect.
Start over and this time, after subdividing the
surface of the cube, deselect all vertices then create
a vertex group. Repeat the process, again selecting
“Tex” in the “Modifiers” tab, and this time select
“Group” in the “Vertex Groups” slot of the modi-
fier. Now, only the vertices in the vertex group are
displaced (Figure 12.60, right).
Figure 12.61
Figure 12.62
12.4.5 Hook Modifiers
The hook modifier allows you to manipulate or animate se-
lected vertices of a mesh while in object mode. Vertices are
assigned (hooked) to an empty object that can be moved in
object mode by pulling the selected vertices with it. This can
be use for a static mesh deformation or the movement can be
animated.
Let's move one corner of a cube. Start with the default scene
with the cube object selected. Tab to edit mode and deselect
all vertices with the A key, then select one vertex (corner) by
pressing it with the RMB. Press Ctrl + the H key and select
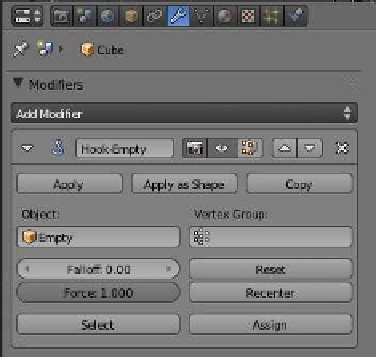
“Hook to New Object” (Figure 12.61). An empty is added to
the scene (orange line under the widget), and by going to the
properties window - “Object Modifiers” button, you will see
that a hook modifier has been added named “Hook-Empty”
(Figure 12.62). Select and move the empty in object mode
and you'll see that the cube deforms (Figure 12.63).
Figure 12.63
An empy has
been added.
In edit mode, you can move the corner of
the cube away from the empty. However,
when the empty is selected and moved in
object mode, the corner follows.