Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
a
b
MIPS/W
Performance
(MIPS)
10000
10000
6000
PC/
Server's
4500
1050
1000
720
300
1000
100
100
30
Embedded
100
0.01
0.1
1
10
100
10
SH1,2
SH3
SH4
SH-Mobile
Power Consumption (W)
1992
Æ
* MIPS: based on Dhrystone 2.1
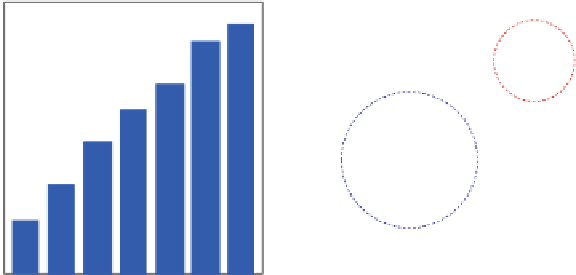
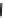
MIPS/W of SH microprocessors
Comparison of MIPS/W
Fig. 1.6
MIPS/W of embedded processors
Fig. 1.7
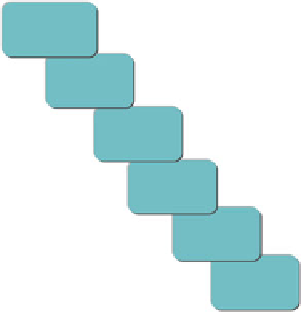
Various processor
High
Hardware
Acc.
cores
Highly
SIMD
Dynamic
Reconf.
Media
Proc.
Special
Purpose
Processor
DSP
CPU
Low
Low
High
Flexibility
6,000 MIPS/W, which was 200 times higher than that of 15 years ago. When we
compare this with the other types of processors in Fig.
1.6b
, we can see the excellent
power efficiency of the embedded processor [
2
] .
Our other policy is to effectively use heterogeneous parallelism to attain high
power efficiency in various digital-convergence applications. Now, various types of
processor cores other than CPU cores have been developed. Figure
1.7
shows exam-
ples of these processor cores, which are positioned in terms of flexibility and perfor-
mance per watt/performance per area.
The CPU is a general-purpose processor core and has the most flexibility. The
other processor cores are developed for special purposes. They have less flexibility



















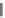



Search WWH ::

Custom Search