Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 6.2 Conjugative plasmids of
E. faecalis
.
Plasmid
Size (kbp)
Phenotype
a
pAD1
60
cAD1 responsive, Hly/Bac
pAM323
66
cAM323 responsive, Em
r
pAM324
53
cAM324 responsive
pAM373
36
cAM373 responsive
pAM
γ
2
∼
60
cAM
γ
2 responsive, Bac
pAM
γ
3
∼
60
cAM
γ
3 responsive
cCF10 responsive, Tc
r
pCF10
54
cIP1017 responsive, Km
r
,Sm
r
pIP1017
?
pIP1141
?
cIP1141 responsive
cIP1438 responsive, Cm
r
,Em
r
pIP1438
?
cIP1440 responsive, Tc
r
,Sm
r
pIP1440
?
pJH2
59
cAD1 responsive, Hly/Bac
pMB1
?
cCF10 responsive
pMB2
?
cPD1 responsive
pMV120
?
cMV120 responsive
pOB1
71
cOB1 responsive, Hly/Bac
pPD1
56
cPD1 responsive, Bac
pYI2
?
cYI2 responsive, Hly/Bac
pYI7
?
cYI7 responsive, Bac
a
Hly; hemolysin, Bac; bacteriocin, Tc
r
; tetracycline resistance, Em
r
; erythromycin
resistance, Km
r
; kanamycin resistance, Sm
r
; streptmycin resistance, Cm
r
; chloram-
phenicol resistance.
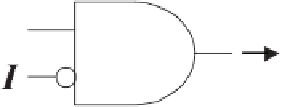
on the state of the input signals, the plasmid
P
i
is either released or not released
from the gate. In the presence of
C
i
(and the absence of
I
i
), the gate releases
P
i
.
The gate can be multiplied in parallel with a variety of the conjugative plasmids
(Figure 6.3).
Conjugative Plasmid Transfer
The
E. faecalis
strains and plasmids used in this study are listed in Table 6.3.
To unify the strains of
E. faecalis
, we transferred the conjugative plasmid
pCF10 from
E. faecalis
strain OG1SSp to strain OG1RF and transferred plas-
mid pAM714 from strain OG1X to strain OG1RF. The procedure for plasmid
Figure 6.2
A primitive gate-unit of
E. faecalis
information gate.