Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
2 Julia Set Escape Time Algorithm Based on Newton Iterative
Algorithm
2.1 The Basic Theory of Escape Time Algorithm
Supposing there is an integer N, and it is big enough, when iterative number of an
initial point
in un-escape area M is less than N, the initial point arrives at the
boundary of un-escape area M and even goes beyond the boundary, then, the initial
point is thought escaping. Otherwise, we think the initial point is a point of
convergent area A. Boundary graphics of A can be drawn by this method. It is the
basic idea of escape time algorithm.
Obviously, the value of N affects quality of drawing directly. If the value of N is
too small, only smaller points can escape, then, the points which do not belong to
convergent area A are kept, and the graphics
we got is rough and not exact.
Contrarily, if the value of A is too big, some points on A will escape, the graphics will
be fuzzy. Appropriate value of A depends on debugging over times and experimental
accumulation [4].
α
Fig. 1.
The schematic diagram of escape time algorithm
2.2 Julia Set Escape Time Algorithm Based on Newton Iterative Algorithm
Newton iteration is proposed in seventeen century by Newton, it is a method to get
root of equation which depends on easy calculation.
If we know
x
is the approximate root of function
f
(
x
)
=
0
, it closes to the real
'
f
(
0
x
)
=
0
f
(
0
x
)
=
0
root of the function. So,
and
can be calculated easily.
'
x
is closes to the real root
x
, so derived function
f
(
0
x
)
Because,
can be replaced
f
(
x
)
=
0
approximately. Because
, so,
−
f
(
x
)
'
f
(
x
)
=
0
(1)
0
x
−
x
0
So,
f
(
x
)
x
−
x
=
−
0
(2)
0
'
f
(
x
)
0


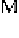

Search WWH ::

Custom Search