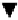Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
Input of plant
litter
4.0 t C ha
-1
(100%)
Lost from
soil as CO
2
2.8 t C ha
-1
(70%)
Incorporated
into new humus
1.2 t C ha
-1
(30%)
Reservoir of
C in soil
humus
72 t C ha
-1
Loss of CO
2
1.2 t C ha
-1
Figure 8 Typical annual turnover of organic matter in a temperate grassland soil at
steady state receiving 4 t C ha
1
All of these compounds do, however, have similar overall properties due
to the preponderance of carboxylic and phenolic functional groups on
the humic polymer. Both of these groups can ionize by losing a hydrogen
ion to give a negatively charged group. This is a variable charge, the
magnitude of which varies with pH, but is always negative and forms
part of the CEC of a soil (see Section 5.5).
R-COOH
R-COO
þ
H
1
"
(5.5)