Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
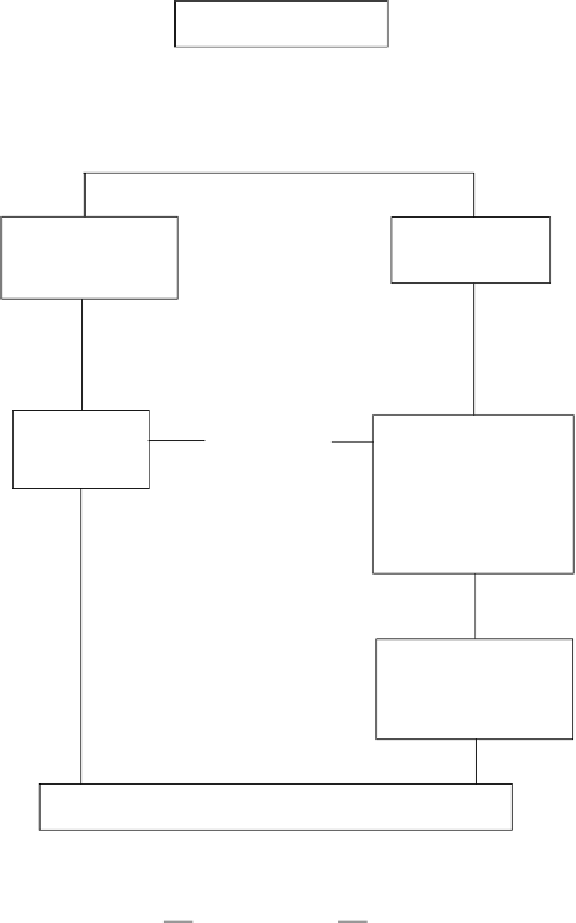
Input of plant residues
Attack by microorganisms
and soil fauna
Resistant material-
poorly degraded
Easily degraded
material
Reaction of
simple
organics with
partially
degraded
material
Partially
degraded
material
Loss of CO
2
, simple
inorganic ions (NO
3
-
etc.) and release of
simple organic
compounds, e.g. amino
acids, sugars and
polyphenols
Microbial activity
Reaction between
simple organic
compounds to form
more complex
polymers
Soil humic material
Figure 9 Possible pathways for formation of humic material in soil from inputs of plant
residues
O
−
+ H
+
ð
5
:
6
Þ
OH
The pK of Equation (5.5) is in the range 3-5, and of Equation (5.6) in the
range 7-8. Thus, carboxyl groups are important in acid soils, while
phenolic groups become important above pH 7.