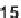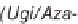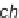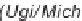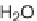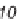Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
SCHEME 2.1
Andreana's use of bifunctional substrates in an Ugi reaction leading to a
subsequent Michael-type cyclization.
isocyanides (Scheme 2.3) [22]. It is worth mentioning that spirocyclic systems are
found in a wide variety of natural products; thus, a number of synthetic methods have
been devised for the synthesis of this scaffold [23]. Spirobenzofurans in particular
have garnered attention due to their biological properties, a notable example being the
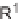
antifungal drug griseofulvin (
28
), which has been reported to have antiproliferative
effects in cancer cells [24].
A Mumm rearrangement is the last step in the Ugi reaction, and Basso et al.
[25] have been able to interrupt (i.e., precluding the Mumm rearrangement) the Ugi
reaction by restricting the amine and acid components within a single molecule. As
a result, the Mumm rearrangement cannot proceed because of strain in the potential
intermediate. The opportunity to use the interrupted Ugi product as an acylating
agent is therefore accessed in this reaction (Scheme 2.4). These reactions are run in
methanol; thus, the acyl product formed is a methyl ester.
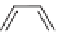
SCHEME 2.2
Andreana's use of bifunctional substrates in a Ugi/Michael/aza-Michael cas-
cade reaction leading to the formation of a complex fused azaspiro-tricycle.