Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
9.4 BRANCHING PATHWAYS IN THE SYNTHESIS OF NATURAL
PRODUCT-LIKE LIBRARIES
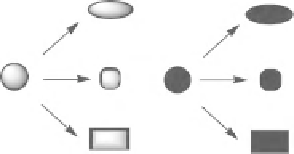
The branching pathway strategy involves the conversion of common precursors into a
range of distinct molecular scaffolds (Scheme 9.11). The development of a branching
pathway may require considerable optimization of the individual skeletal transform-
ing steps. It is important, however, to ensure that the ethos of diversity-oriented
synthesis be retained: that is, that a library be prepared in a deliberate and simulta-
neous fashion. In some cases the implementation of an intricate branching pathway
which exploits a very limited range of precursors may cause the parallel nature of
diversity-oriented synthesis to be lost.
Complementary metal-catalyzed branching pathway which exploits complemen-
tary cyclization reactions (Scheme 9.12) [29]. A four-component Petasis condensation
reaction was used to assemble flexible cyclization precursors (e.g.,
79
). Alternative
cyclization reactions were then used to yield products with distinct molecular skele-
tons: Pauson-Khand reaction (
→
80
); Pd-catalyzed cyclization (
→
81
); Ru-catalyzed
cycloheptadiene formation (
→
82
); base-induced cyclization (
→
83
); Au-catalyzed
cyclization of the alcohol onto the alkene (
→
84
); enyne metathesis (
→
85
); and
Meisenheimer [2,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement (not shown).
Many of the initial cyclization products could be exploited in the synthesis of
additional molecular scaffolds. For example, Diels-Alder reactions with 4-methyl-
1,2,4-triazoline-3,5-dione converted dienes (such as
85
) into polycyclic products
(such as
86
) (Scheme 9.12). In addition, four of the cyclization reactions could be
used again to convert the enyne
83
into molecules with four additional skeletons (
87
to
90
) (Scheme 9.13). The key to this powerful synthetic approach lay in the design
of precursors (e.g.,
79
), which were effective substrates in a wide range of efficient
and diastereoselective cyclization reactions.
Painter et al. prepared a library of alkaloid-like compounds designed to target
a large region of biologically relevant chemical space as efficiently as possible
(Scheme 9.14) [30]. The approach focused on the broad chemistry of derivatives of
the allenylated tryptophan analogs
91
. A range of complementary transition metal-
catalyzed reactions was used to convert the allene-ynes
92
into alternative scaffolds:
for example, complementary Mo- and Rh-catalyzed cyclocarbonylations gave the
regioisomeric cyclopentenones
94
and
95
, respectively, and thermal [2
2] cycload-
dition gave the corresponding cyclobutenes
96
. Pictet-Spengler reactions were used
+
SCHEME 9.11
Overview of the branching pathway strategy in which common substrates
are converted into alternative scaffolds under reagent control.