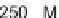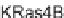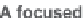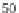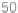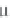Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
SCHEME 4.31
Representative GGTI compounds obtained from a DOS library based on
phosphine catalysis.
Lerner, and co-workers prepared peptidomimetic inhibitors of GGTase-I (GGTIs)
derived from the
CAAL
peptide [95,96], further development of compounds that
inhibit GGTase-I and RabGGTase is desirable because they will provide novel
reagents to deepen our understanding of protein geranylgeranylation.
With this premise in mind, we screened our pilot library compounds for their
ability to inhibit the activity of human GGTase-I to geranylgeranylate K-Ras4B or
RhoA. We identified a number of compounds as GGTIs; they shared two types of
unique novel scaffolds (Scheme 4.31) [63,65-67]: one group containing the guvacine
ring as its core scaffold and the other containing a pyrroline ring as its core scaffold.
To further improve the efficacy of the GGTIs and to explore their structure-activity
relationships, we prepared a focused library of 4288 GGTI analogs through solid-
phase synthesis in a split-pool manner (Scheme 4.29).
Screening of the focused library resulted in identification of the GGTIs
111b
and
115b
, which exhibited submicromolar values of IC
50
. Notably, compound
115b
did
not induce any significant inhibition of FTase or RabGGTase, even at concentrations
of 50
M. At the same time, we found that coupling the carboxyl group of the
dihydropyrrole ring of compound
111b
with phenylalanine derivatives significantly
improved the cellular activity (Scheme 4.32). Furthermore, to examine the speci-
ficity of GGTase-I inhibition by compounds
111b
and
115b
, we also tested their
inhibition behavior toward two closely related enzymes: FTase and RabGGTase. Sur-
prisingly, compound
111b
induced slight inhibition of RabGGTase at concentrations
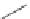
greater than 10
M. With this trail, the rescreening of the focused library resulted in
identification of inhibitors of RabGGTase (RabGGTIs). As indicated in Table 4.12,
compounds
113a
to
e
(Scheme 4.33) inhibited RabGGTase with IC
50
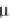
values of 2
to 5
M, whereas their inhibition of GGTase-I and FTase required concentrations
greater than 50
M, respectively. Compounds
113a
to
e
are
the first potentially useful inhibitors of RabGGTase [97-99].
M and greater than 100