Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Flow circuit
Oxygen
Reservoir
Peristaltic
pump
Bioreactor
Flow inlet
Inlet media
chamber
(not modeled)
Bioreactor
Flow outlet
via the Outlet
Media Chamber
(not modeled)
Velocity
Shear stresses
Y
Z
X
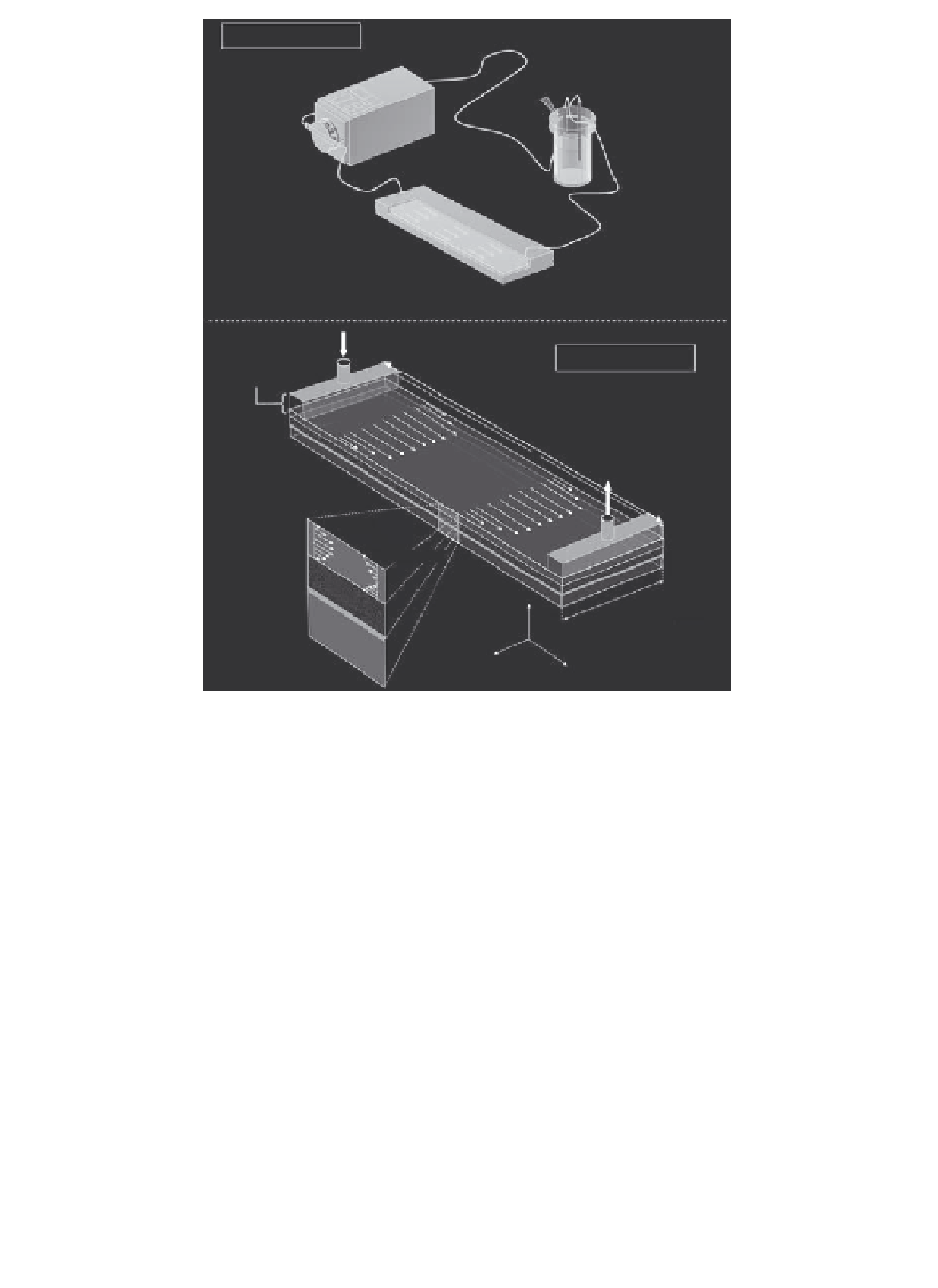
FIGURE 3.13
Sketch of the parallel-plate bioreactor designed to apply a given level of fluid-
flow-induced shear stress to tissue-engineered articular cartilage. Noticeable
improvement in matrix composition and mechanical properties of the native
tissue seeded with chondrocytes was reported (Gemmiti and Guldberg 2006).
Mechanical stimulation of the cells as well as enhanced nutrient mass transport
associated with the hydrodynamic environment of this system design may
reveal to be an effective functional strategy in tissue engineering.
Four different cases, corresponding to the stimulation phases of the thinner
and thicker tissues as well as the controls (kept in the preculture conditions),
were investigated (see Figure 3.14).
The basic convection-diffusion-reaction equations of the nutrient trans-
port model introduced in Section 3.4.2 have been adapted to this bioreac-
tor schematically designed in two dimension. It is thus possible to simulate
the time evolution of the space variations in oxygen concentration within the
engineered cartilage tissue. In the upper chamber flow channel, neglecting the
Search WWH ::

Custom Search