Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
0.6
1.2
0.5
1
0.4
0.8
0.3
0.6
0.2
0.4
0.1
0.2
0.0
0
0 0 0 0
speed (mm/min)
80
100
120
B
C
D
E
Modified Surfaces
downstroke
upstroke
I
II
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
0
200
400
600
800
Time (hrs)
A
B
C
D
III
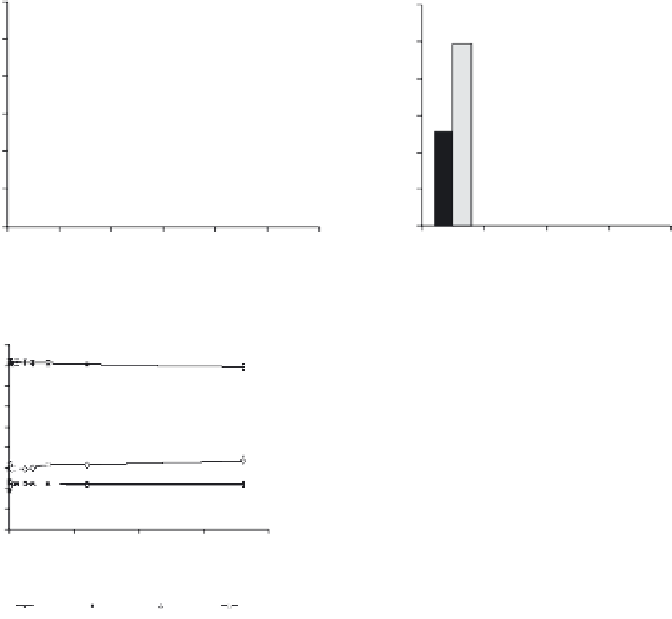
Figure 20.4.
The effect of speed on transfer ratio of the monolayer (I)
; monolayer of
(PTC : Chol) (1 : 0.7) during upstroke,
Transfer ratio of the monolayer with different composi-
tions (II)
; during downstroke and upstroke of the polymer fi lm vertically at the interface; PTC
(B), (PTC : Chol) (1 : 0.7) (C), (PTC : Chol) (1 : 0.35) (D), (PTC : Chol : GalC) (1 : 0.35 : 0.125) (E). The
surface pressure was maintained at 30 mN/m for all the monolayers during deposition.
Stabilil-
ity studies under low shear stress conditions (III)
; PMMA Bare (A), OCMC (D). PMMA modifi ed
with OCMC-AH (B), OCMC-AHP (C) (B).
for further detailed characterization. This monolayer showed a compact surface,
as evident in Figure 20.3D (1).
20.3.6 Surface Properties of Supported Thin Solid Films
The contact angle
is reduced from 85 ° to 20 ° during surface modifi cation. The
stability studies were done under low shear conditions. Figure 20.4(III) shows the
stability studies of the modifi ed surfaces, represented in terms of the change in
contact angle. The polymeric surface modifi ed with the ternary lipid layer shows
less stability as compared to the laterally stabilized surfaces. In this surface the
θ



Search WWH ::

Custom Search