Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
contact angle have been stabilized after a certain period, may be due to the
improved stability contributed by the Chol and GalC (condensation effect).
However, in the case of polymer surface modifi ed with ternary lipids containing
anchors (Figures 20.4IIIB and C) the contact angle has not varied signifi cantly
with time. This shows that the anchored lipid layers are much more stable on the
polymer surface than the unanchored lipid layers.
20.3.7 Biological Interactions onto These Surfaces
Further characterizations of the supported lipid layers are done only for those
with improved stability by the lateral stabilization using anchors of albumin,
heparin, and PEG. The surface morphology of the optimized PC modifi ed surface
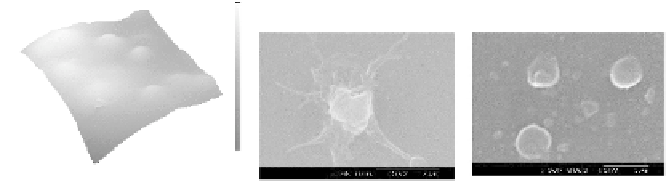
was studied using AFM in contact mode in air. Figure 20.5(I) shows the contact
mode AFM image of the PC surface modifi ed with optimized lipid composition,
in air. The surface shows a smooth texture with domains of the size range of 50-
100 nm. No holes or uneven regions were observed on the surface.
A
1
2
mH
3
150
B
2
100
3
1
mH
25000
20000
15000
10000
5000
50
C
1
25000
2
20000
3
15000
0
10000
5000
0
0
(III)
(II)B
(I)
(II)A
300
250
200
150
100
50
0
ABC
Modified surfaces
Platelet
DE
(a)
(b)
Leucocyte
Erythrocyte
(IV)A
(IV)B
(V)
Unmodified
surface
Closely
packed
ordered
hydrophobic
surface
Loosely
packed
ordered
hydrophobic
surface
Closely
packed
ordered
hydrophobic
surface
P
C
P
C
I
I
Protein
adsorption
Blood cell
adhesion
(VII)
(VI)







Search WWH ::

Custom Search