Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
The advantage of the phase separation technique is that it is a relatively
simple technique that is not equipment intensive. In addition, a highly-porous
structure can be obtained with control over the mechanical properties of the
nanofi brous matrix and batch to batch consistency can be easily maintained [62].
However, a disadvantage of this technique can be limited control on the internal
architecture of the nanofi brous matrix [67] .
13.3.3 Electrospinning
Electrostatic spinning (electrospinning) is the synthesis of fi bers of diameter
ranging from 10 nm to 10
m or larger by drawing it from a polymer solution
under the infl uence of electrostatic forces [68,69]. The concept of electrospinning
is more than 100-years-old [70-76] and has regained the attention of researchers
for the synthesis of nanofi ber-based scaffolds for tissue engineering applications.
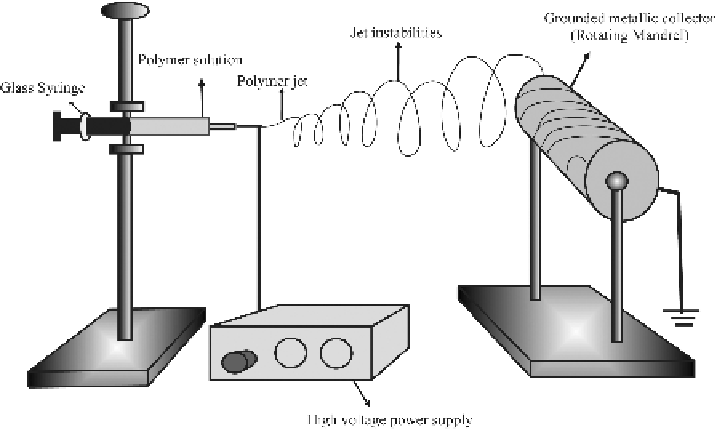
The apparatus for electrospinning (Figure 13.4) consists of a syringe which is
the reservoir for holding the polymer solution, capillary/needle, high voltage
power supply, grounded metallic collector (plate/mandrel), and a syringe pump
(not shown in the fi gure) that pumps the polymer at a particular rate from the
needle tip. The presence of a syringe pump is not mandatory when the syringe is
placed in a vertical confi guration, whereby the polymer solution is released from
the capillary under the infl uence of gravity. Further, the collector can either be a
grounded metallic plate that is stationary or a rotating cylinder, depending on the
requirement of a non-woven mesh or aligned fi bers, respectively.
During electrospinning, a polymer solution is taken in a glass syringe con-
nected to a metallic needle. The polymer solution by virtue of its viscosity/surface
μ
Figure 13.4.
Schematic of the electrospinning technique.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search