Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Al
2
O
3
Al
2
O
3
/ ZrO
2
Al
2
O
3
(a)
(b)
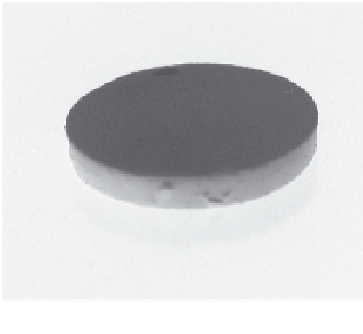
Figure 10.5.
Schematic illustration of the desired Al
2
O
3
/FGM/ZrO
2
-Al
2
O
3
/FGM/Al
2
O
3
profi le
(a) and a sintered FGM disc made by EPD (b). [Anné, 2005a].
the achievable compressive stresses at the surface of the FGM cup inserts and
ball-heads, FGM discs are processed by EPD and analyzed. The gradient profi les
are comparable to those to be generated in the hip-prosthesis components. The
plates are also used for the densifi cation studies and for property assessment so
that the effects of the gradient on the overall strength and wear resistance can be
determined. Discs with a thickness
36 mm after sintering
are processed. The sintering and microstructural evaluation of the Al
2
O
3
/ZrO
2
FGM components is discussed in section 10.6.
Flat discs with a symmetric or semi-symmetric gradient profi le, going from a
pure Al
2
O
3
surface layer to a homogeneous ZrO
2
/Al
2
O
3
composite core with
intermediate graded zones are made by means of EPD (Figure 10.5).
The procedure for depositing functionally graded discs by EPD, involves:
>
5 mm and a diameter
>
1. The development of a suitable suspension for EPD, as discussed above.
2. The design and construction of a cell with the proper dimensions.
3. The development of a mathematical model to predict the composition
profi le of the FGM discs.
4. The processing of a green FGM disc, according to the mathematical
model.
5. Drying of FGM discs.
6. Sintering.
10.5.2 Mathematical Model to Predict the Composition Profi le of
FGM Discs
Vandeperre [Vandeperre et al., 2000] developed a kinetic model to predict the
current and deposition kinetics in EPD. Put et al. further developed this model to


Search WWH ::

Custom Search