Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
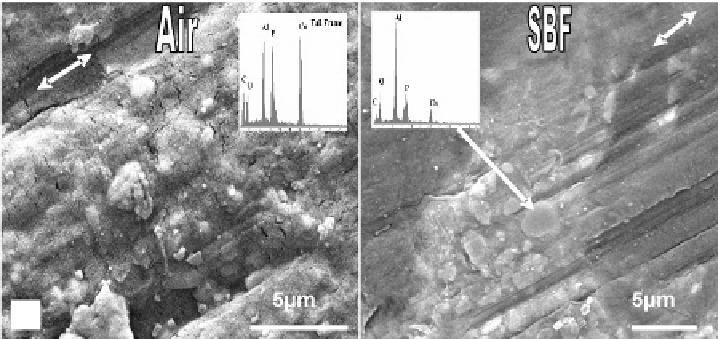
(a)
(b)
Figure 3.11.
SEM images revealing evidence of abrasion on as-fretted/worn surface of HDPE-
20 vol% HAp-20 vol% Al
2
O
3
in two different environments: air (a) and SBF (b). Fretting condi-
tions: 100,000 cycles, 10 Hz frequency, 10 N load and 80
μ
m stroke length. counterbody: 10 mm
diameter zirconia ball. EDS results of the noticeable tribological features are depicted as in-
serts in the corresponding micrographs
95
.
growth on the implanted surface. The mechanism of fi broblast cell attachment to
the sample surface is guided by the interaction of protein receptors in cell mem-
brane with cell adhesion proteins. Also, cell adhesion protein originates from the
plasma and physiological fl uid. Protein receptors on the cell surface enhance cell
attachment to the biocompatible sample surface. These receptors transduce bio-
chemical signals to the nucleus by activating the same intercellular signaling path-
ways used by growth factor receptors. The more rapid the cells spread, the higher
their rate of proliferation
98
. The presence of hydroxyapatite or similar biocompat-
ible materials stimulates the above cell growth functions, culminating in cell pro-
liferation throughout the sample surface.
3.6 METALS AND ALLOYS IN BIOMEDICAL APPLICATIONS
Because of better physical properties such as strength, toughness, or ductility,
some biocompatible metals and their alloys are often used for joint and bone
implants. The applications of metals include bone replacement, bone repair, met-
al plates for fractures, dental implants (fi llings and posts), screws and staples,
parts of other devices like artifi cial hearts, pacemakers and catheters. The major
issues for metallic implants are biocompatibility, wear resistance and corrosion
resistance in body fl uid. In the following sections, such issues will be discussed
fi rst, followed by a discussion on the properties and applications of various im-
plant metals and alloys in reference to literature discussed earlier.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search