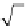Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
and.
z
.denote.the.actual.radial.and.axial.coordinates.in.the.focal.region..Now.we.consider.a.speciic.pupil.
function.that.has.uniform.amplitude.
A
ξ η
(
,
)
=
1
.and.contains.the.Zernike.terms.corresponding.to.tip,.
tilt,.and.defocus.only:
(
)
.
.
P
( ,
ξ η
)
=
exp
j M Z
( ,
ξ η
)
+
M Z
( ,
ξ η
)
+
M Z
( ,
ξ η
)
(5.6)
2
2
3
3
4
4
Here.the.corresponding.Zernike.polynomials.in.Cartesian.coordinates.are.deined.as
.
Z
=
2
ξ
,
Z
=
2
η
, and
Z
=
3 2
( (
ξ
2
+
η
2
)
−
1
)
.
(5.7)
2
3
4
When.we.introduce.Equation.5.6.into.Equation.5.3.and.compare.the.coeicients.in.the.arguments.of.the.
exponentials,.we.ind.that.the.aberration.modes.(Equation.5.7).efectively.introduce.a.shit,.Δ,.in.the.
x
,.
y
,.and.
z
.directions,.given.by
M
n
M
n
M
n
3
λ
λ
α
λ
2
3
4
.
∆
x
= −
,
∆
y
= −
,
∆
z
=
sin (
α
/2)
.
(5.8)
π
sin
α
π
sin
2
π
2
he. above. expressions. allow. one. to. calculate. the. displacement. of. the. focal. spot. directly. from. the.
Zernike.mode.coeicients.for.tip,.tilt,.and.defocus.extracted.from.
Ψ ξ η
,
( )
.
he.calculation.of.the.spot.shape.and.position.from.the.wavefront.as.expressed.in.Equation.5.3.is.an.
approximation.that.is.valid.only.for.relatively.small.variations.in.refractive.index..We.also.note.that,.for.
high-NA.lenses,.defocus.is.represented.by.a.pupil.function.consisting.of.even-order.polynomials.includ-
ing.the.terms.in.ρ
4
.and.higher.orders..In.Equation.5.3,.we.have.approximated.defocus.by.the.dominant.
quadratic.term.
5.5 results and Discussion
To.quantify.the.specimen-induced.distortions,.we.processed.wavefront.data.from.a.variety.of.biological.
specimens;. the. specimen. characteristics. are. listed. in. Table. 4.2. of. Chapter. 4.. We. chose. examples. that.
represent.common. specimen.categories.. For.confocal.or.multiphoton. techniques,.high-NA.lenses.are.
usually. preferred. because. of. their. superior. light. collection. eiciency. and. resolution.. However,. some.
applications.may.require.lower-NA.lenses,.and.therefore.we.investigated.the.efect.of.specimen-induced.
distortions.at.lower.NA.as.well..In.both.cases,.the.wavefront.information.was.extracted.from.the..data.
sets.recorded.with.a.1.2.NA.water-immersion.lens..For.the.lower.NA,.a.smaller.circular.subregion.of.the.
interferograms.corresponding.to.an.NA.of.0.6.was.analyzed,.and.the.Zernike.modes.were.itted.to.this.
subregion.using.the.same.procedure.
he.local.displacements.of.the.focal.spot.calculated.using.the.aforementioned.method.are.displayed.
in.
Figure.5.3
.
for.the.NA.of.1.2.and.in.
Figure.5.4
.
for.the.lower.NA.of.0.6..For.each.specimen,.the.devia-
tions.in.the.
x
,.
y
,.and.
z
.directions.are.shown.separately..Statistical.values,.such.as.the.individual.standard.
deviations.in.the.
X
,.
Y
,.and.
Z
.directions,.are.listed.in.
Table.5.1
.
.he.maximum.value.of.the.total.spatial.
deviation.
d
2 2 2
.for.each.specimen.is.also.given.in.
Table.5.1
.
he.total.3D.displacement.of.the.spot,.depending.on.the.specimen.structure.and.location.within.the.
specimen,.can.exceed.1.μm..he.patterns.observed.correlate.with.the.specimen.structures.as.expected..
For.example,.the.scan.of.specimen.no..1.contains.the.horizontal.edge.of.the.tissue,.which.causes.distor-
tion.in.the.
y
.and.
z
.directions.but.leaves.the.
x
.component.almost.unafected..he.largest.distortion.value.
in.the.order.of.2.μm.was.found.within.a.particular.region.of.the.mouse.oocyte.cell.(specimen.no..2).at.
an.NA.of.0.6,.where.the.axial.component.was.dominant.
To.understand.the.inluence.of.the.NA.on.the.specimen-induced.distortions,.we.turn.to.the.illustra-
tions.of.
Figure.5.5
.
.Here.cross.sections.Ψ(
r
).of.two-dimensional.phase.functions.Ψ(
r
,θ).in.the.pupil.plane.
of.the.lens.are.shown.for.three.diferent.situations..Using.a.lens.of.larger.NA.is.equivalent.to.capturing.
=
∆
x
+
∆
y
+
∆
z