Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
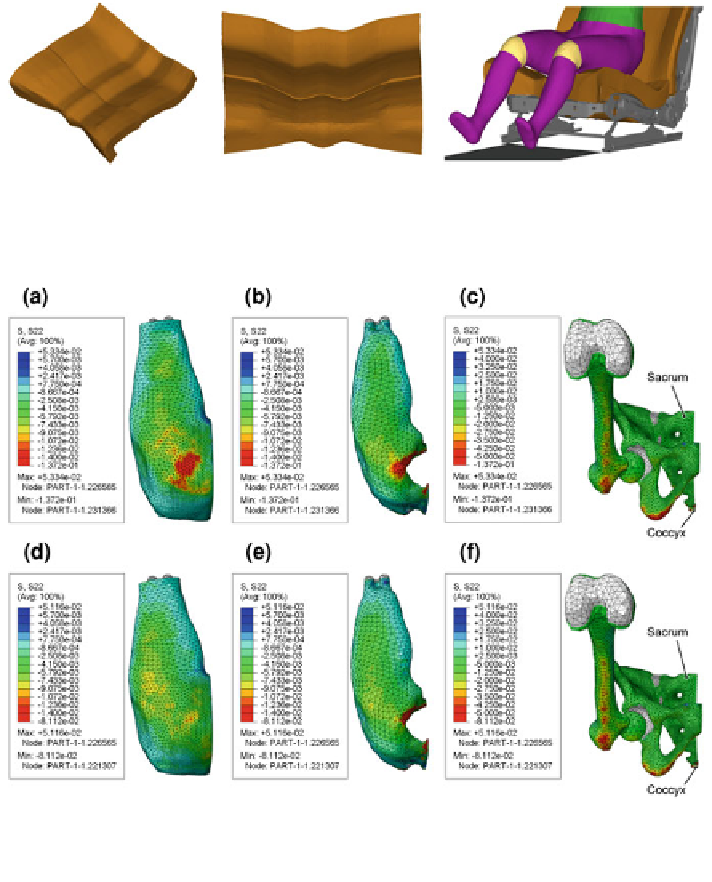
Fig. 7.75 3D-seat surface from different perspectives (left and center) and with a female Boss-
Model (right)
Fig. 7.76 Vertical direct stress S
22
distribution (a, d) at skin level, (b, e) at the fat-muscle
interface and (c, f) at the bone surface, resulting from interaction between the female Boss-Model
and the non-optimized (a, b, c) as well as the optimized transopt cushion variation (d, e, f)
Maximum tissue stress occurred beneath the ischial tuberosity. All three
compressive stresses S
ii
(i = 1, 2, 3), as well as the (positive) shear stress
component S
12
were reduced by approximately 35 % and the (negative) shear stress
S
12
by nearly 50 % (cf. Figs.
7.72
b,
7.74
). The three tensile stresses S
ii
(i = 1, 2, 3),
however, were higher with the optimized cushion shape (cf. Fig.
7.72
b).
Generation of the Optimized Seat Surface in Three Dimensions: Based on
the separate procedures, i.e. seat surface optimization in the transversal and sagittal