Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
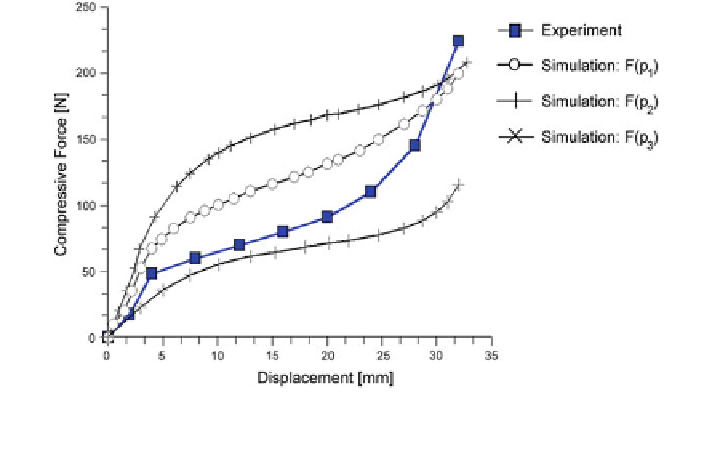
Fig. 3.33 Force-displacement curves recorded from uniaxial compression experiment and
simulation outputs in the parameter optimization process of polyurethane soft foam material
As already mentioned, the least-square approach aims to minimize the sum of
the deviations squared from a given set of data. Generally, a weighted least-square
problem can be formulated basically following (
3.364
) as given in (
3.385
).
U
w
ð
p
Þ
:
¼
X
n
2
¼
!
g
i
f
i
h
i
; ð Þ
f
i
ð
h
i
Þ
min
ð
3
:
385
Þ
i
¼
1
Using the expressions introduced in Fig.
3.31
, the unweighted least-square
problem thus reads as given in (
3.386
).
h
i
2
U
k
ð
a
k
;
p
;
m
k
;
p
;
...
Þ
:
¼
X
n
k
;
i
ð
a
k
;
p
;
m
k
;
p
;
...
Þj
u
i
F
exp
F
sim
k
;
i
j
u
i
ð
3
:
386
Þ
i
¼
1
In (
3.385
) U
w
ð
p
Þ
denotes the weighted sum of squared (vertical) residuals
where the bracket term f
i
ð
h
i
;
p
Þ
f
i
ð
h
i
Þ
is defined as moduli of the i-th residual,
f
i
ð
h
i
;
p
Þ
is the model function including the adjustable parameters p
i
held in the
parameter vector p and the h
i
as independent variables, the f
i
are dependant
variables obtained through experiments, g
i
is the weight factor of the i-th point.
They account for appropriate influence of data points and unequal variance,
respectively; n is the number of sampling points.
In (
3.386
) the squared vertical difference of simulated discrete force values F
sim
i
and experimentally measured force values F
exp
i
at consistent displacements u
i
is
derived for iteration step k.