Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
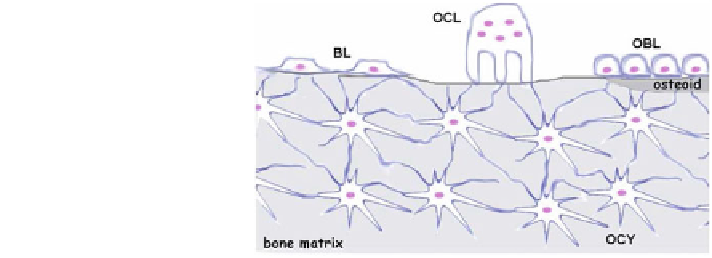
Fig. 3 Schematic
representation of the four
bone cells types (reproduced
with permission from [
82
])
total bone mass, cortical tissue permits the locomotion, stores and releases
chemical elements like calcium or phosphorous and protects the organs.
The cortical unit structure, called osteon, is a cylinder whose radius is about
10
4
m (see Fig.
2
b). An osteon is constituted by the collagen-apatite matrix
containing vascular porosity (Haversian and Volkmann's canals) and elliptic holes
named lacunae. Each lacuna holds one mechanical sensor cell (osteocyte, see
Fig.
2
d) swimming in fluid environments. These osteocytes develop within little
channels (canaliculi) connecting them together and so forming a stellar network
within bone volume (see Fig.
2
c). At the microscale, the representative volume is a
fraction of the lacuno-canalicular system (see Fig.
2
e). Canaliculi are described by
two concentric straight cylinders whose the cross section is circular with radii R
C
and R
M
such as R
C
[ R
M
:
The interstitial fluid occupies the annular space between
the canalicular wall and the osteocyte process membrane. The canaliculus length is
noted L
C
:
Since the radii of the osteocyte and of the canaliculi vary with age,
species, bone location, osteocyte age, etc. [
26
], a major difficulty in modelling
consists in the allocation of these values. Thus if R
C
¼
130
65 nm for mice
[
170
], for sheep and dogs R
C
ranges from 100 to 500 nm [
66
,
129
]. As we are
interested in human bone, in this study, we will typically consider the values of
You et al. [
165
], namely R
C
¼
100 nm
:
Since the ratio R
C
=
R
M
has given to be
around 2 [
154
], the value of R
M
will consequently be 50 nm. According to [
165
],
the osteocyte process length is three hundred times its radius, so we typically have
L
C
15
10
6
m.
2.2 Bone Cells
In bone tissues, four types of cells can be distinguished. Figure
3
gives a schematic
representation of the four bone cells types. Multinucleated cells are the osteoclasts
(OCL) which can remove bone. New bone is built by the osteoblasts (OBL) which
can synthesize the osteoid matrix (white zone) which will be mineralized (grey
zone). Some osteoblasts embedded in the bone volume can evolute in osteocytes
(OCY) that are connected with bone lining cells (BL).
Search WWH ::

Custom Search