Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
physical vapor deposition (PVD), and even chemical vapor depo-
sition (CVD). Some non-line-of-sight techniques can treat almost
the entire surface of the scaffolds but only induce the formation
of a bioactive layer without nanophase materials.
21
,
22
Although the
fabrication of nanostructures by layer-by-layer processing
23
pH-
induced self-assembly,
24
colloidal self-assembly,
25
electron beam
lithography (EBL),
20
and interference lithography (IL)
26
have been
proposed,fewstudieshavereportedthenaturalgrowthofbioactive
nanophasematerialsdirectlyonthesurfaceof3Dmacroporousscaf-
folds withcomplex topographies.
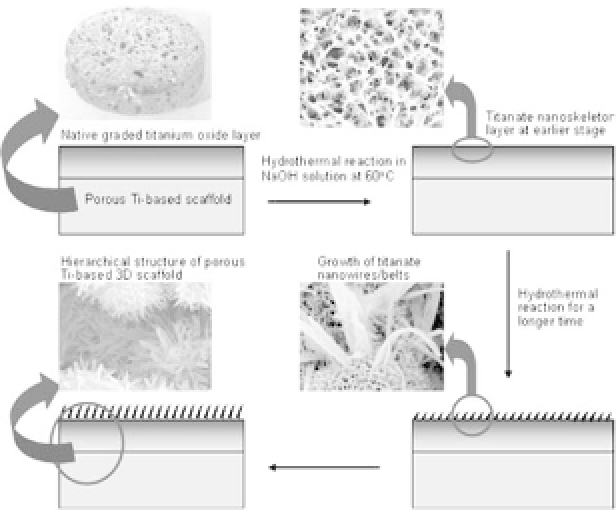
Our recent work reveals that a lower-temperature hydrother-
mal treatment can induce the formation of 1D nano titanates on
the entire exposed areas of 3D porous Ti-based metals such as Ti
and NiTi.
16
This fabrication process of 1D nanowires/nanobelts is
schematically illustrated in Fig. 3.7. The 3D porous Ti-based metal
plates fabricated by CF-HIP are put in a Teflon-lined autoclave in
a concentrated NaOH aqueous solution. The autoclave is heated to
60
◦
C
∼
180
◦
C for different time durations. The treated plates are
washed in deionized water to remove the remaining alkaline solu-
tion and then dried at 60
◦
Cinanoven.Duringtheheatingprocess,
Figure 3.7.
Fabrication process of 1D nanophase materials on Ti-based
metals (NiTi &Ti).
16








Search WWH ::

Custom Search