Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
was created using AUL-TPS initialization and minimizing for 100 iterations with
α
=
0
.
5 and
β
=
0
.
012.
The tables in Fig. 6.5 tabulate the inverse consistency error at four repre-
sentative points in the images. The points
A
and
C
are located at points away
from landmarks while the points
B
and
D
are located at landmark locations. The
inverse consistency error at the landmark points is small for both algorithms.
However, the landmark error is quite large away from the landmark locations in
the UL-TPS algorithm. The range of intensities on the color bar for each method
shows that the range of inverse consistency errors for the UL-TPS algorithm was
in the range of 0.002 to 4.9 pixels while this same error for the CL-TPS algorithm
ranged from 0.00 to 0.009. This shows that the CL-TPS algorithm reduced the
inverse consistency error by over 500 times that of the UL-TPS algorithm for
this example.
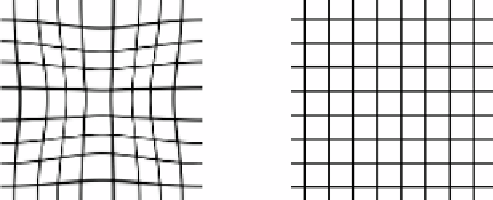
A pair of transformations are point-wise consistent if the composite function
h
(
g
(
x
)) maps a point
x
to itself. Spatial deviations from the identity mapping can
be visualized by applying the composite mapping to a uniformly spaced grid. The
grid is deformed by the composite transformation in regions where the forward
and reverse transformations have inverse consistency errors. The composite
transformation does not deform the grid for a perfectly inverse consistent set
of forward and reverse transformations. Fig. 6.6 shows the composite mapping
Figure 6.6: Deformed grids showing the error between the forward and reverse
transformations estimated with the landmark-based thin-plate spline algorithm
(left panel) and the CL-TPS algorithm (right panel). The grids were deformed
by the transformation constructed by composing the forward and reverse trans-
formations together, i.e.,
g
(
h
(
x
)). Ideally, the composition of the forward and
reverse transformations is the identity mapping which produces no distortion
of the grid as in the right panel. The fuzziness associated with the grids are due
to the bilinear interpolation.