Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
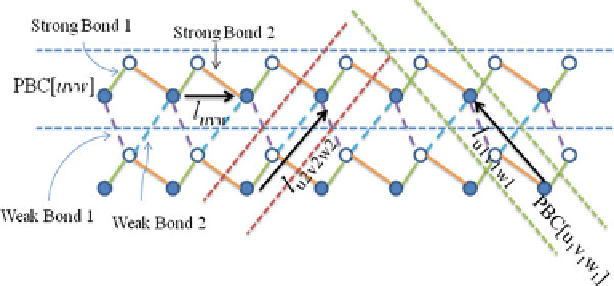
Fig. 2.17
A crystal bond network and the identification of three PBCs
Fig. 2.18
Illustration of F, S,
and K faces of crystals
[
74
-
77
]
•
S-face: Stepped face (roughened face)—one PBC in parallel to the surface is
identified.
•
K-face: Kink face (roughened face)—no PBC in parallel to the surface is
identified.
According to Hartman [
74
-
77
], crystals are bounded by F faces. Here, F faces
correspond to the faceted or flat faces while S and K faces are the roughened faces.
According to definition of F face, there should be an
interconnected
bond network
parallel to an F face (cf. Fig.
2.17
). It follows from the modern statistic physics [
78
]
that there will be a nonzero roughening temperature. For S and K faces, since no
connected
bond network occurs in parallel to the faces, the faces are roughened all
the time. In summary, the PBC analysis includes the following key steps:
1. Calculate/identify various bonds/interactions connecting the neighboring struc-
tural units. (Only the bonds established in the crystallization will be considered.)
2. Indentify the bond structure of the crystals.
3. Identify PBCs and the networks in all directions.
4. Identify F faces.