Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
called CVX-241 (Pfizer) with dual specificity for VEGF and
angiopoetin-2 is in Phase I clinical testing for treatment of
cancer.
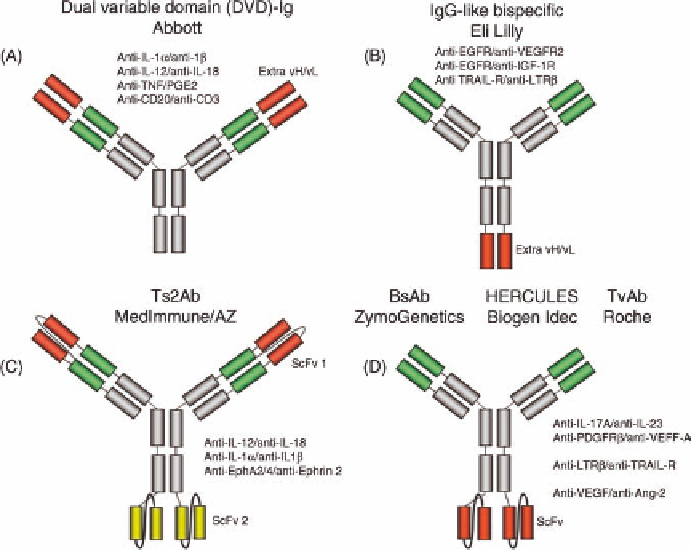
bispecific antibodies target surface receptor combinations
EGFR and IGF-1R, EGFR and VEGFR2, or TRAIL-R and
LTR
b
, respectively [36]. With the acquisition of Imclone,
Eli Lilly gained access to the Di-diabody format for making
bispecific antibodies [37].
Both ZymoGenetics (now BMS) and Biogen Idec have
been fusing single-chain antibodies (scFvs) to the C-termini
of mAb heavy chains (Figure 35.3D). ZymoGenetics has
published a stable bispecific anti-IL-17A/anti-CD23 [38]
and an anti-PDGFR
b
/anti-VEGF-A antibody for treatment
of inflammatory diseases. Biogen Idec is calling their
approach “HERCULES.” Their researchers published on
generation and characteristics of a bispecific antibody where
anti-LTR
b
scFvs were fused either N- or C-terminally to the
heavy chain of an anti-TRAIL-R antibody [39]. Roche also
bought into this format, which they call “TvAb” for tetra-
valent bispecific antibody. One TvAb referred to as TAvi6 has
disulfide bond-stabilized scFvs specific for angiopoetin-2
fused to the C-termini of anti-VEGF mAb bevacizumab
(Avastin
1
) heavy chains [40]. Preclinical data showed supe-
rior antitumor activity in xenograft studies over bevacizumab.
Researchers at MedImmune/Astra Zeneca have been
fusing scFvs also to the N-terminal position of IgG
(Figure 35.3C). This allows design of not only bispecific
but also of trispecific antibodies. A number of bispecific
antibody candidates are in early development that were
35.4 IgG-LIKE BISPECIFIC ANTIBODIES WITH
FUSED ANTIBODY FRAGMENTS
A number of large biopharma companies have approached
the development of bispecific antibodies by fusing extra
variable domains to mAbs (Figure 35.3). For instance,
Abbott is featuring its dual variable domain (DVD) bispe-
cific antibody format [34]. The DVD format is extending the
normal variable domains at the N-termini of heavy and light
chains by two more variable domains and contains a total of
four binding sites per antibody (Figure 35.3A). At least four
early-stage programs have been presented in 2010 [35].
Three bispecific antibodies are neutralizing inflammatory
mediators by DTof IL-1
a
and IL-1
b
, IL-12, and IL-18, or, of
TNF-
a
and prostaglandin E2. A fourth bispecific antibody
with dual specificity for CD3 and CD20 was designed to
redirect T cells for lysis of lymphoma cells.
Researchers at Eli Lilly have fused a second variable
domain to the C-termini of heavy chains (Figure 35.3B),
creating a total of three binding sites per antibody molecule.
In 2010, two early-stage programs were presented where
FIGURE 35.3
IgG-like bispecific antibodies with fused antibody fragments. Red and green colors
highlight variable antibody domains of distinct specificity. Disclosed binding specificities and
particular structural features are labeled. Single-chain antibodies (scFvs) show a peptide linker
between variable domains.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search