Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
these fusion proteins were determined in rodent species.
Following intravenous administration in rats, the pharmaco-
kinetics of both IFN-
a
2b-DOM7h-14 and HSA-IFN-
a
2b
were significantly improved in comparison to unfused
IFN-
a
(Table 11.1). Similar area under the plasma concen-
tration-time curve (AUC) values were obtained for
IFN-
a
2b-DOM7h-14 and HSA-IFN-
a
2b (737.5 and 689.2 h
mg/mL, respectively), which in both cases represents a
significant increase over the value of 18.8 hmg/mL observed
with unfused IFN-
a
. The circulating half-life (T
1/2
elim) of
both fusion proteins was also increased when compared to
that of unfused IFN-
a
standard. In vivo half-lives of IFN-
a
2b-DOM7h-14 and HSA-IFN-
a
2b were calculated at 22.6
and 14.2 h, respectively, which in both cases represent a
significant increase in the circulating half-life of both fusion
proteins when compared to the 1.2 h half-life calculated for
unfused IFN-
a
. When compared directly, the circulating
half-life of IFN-
a
2b-DOM7h-14 is
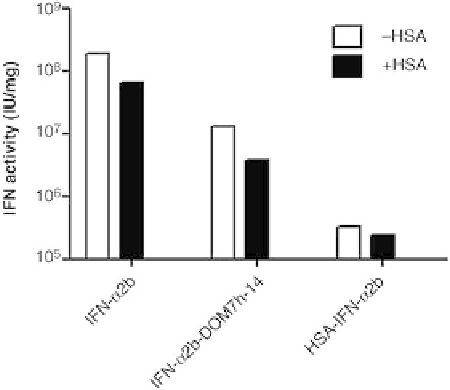
FIGURE 11.4
Antiviral activity of IFN-
a
2b fusion proteins. The
protective effect of IFN-
a
2b-DOM7h-14 and HSA-IFN-
a
2b was
evaluated in antiviral assays using A549 cells infected with EMCV.
Assay was carried out in the presence (black bars) and absence
(white bars) of 100
m
M human serum albumin. For comparison,
data obtained with unfused IFN-
a
2b are also shown.
Source:
Reproduced from Reference [20] by permission of Oxford
University Press.
1.5 times longer than
that of HSA-IFN-
a
2b based on the values calculated from
these experiments.
As clinical preparations of IFN are patient administered
via subcutaneous injection, we also carried out a second
study to determine the pharmacokinetics of AlbudAb and
HSA-fused IFN-
a
, compared to unfused IFN-
a
, following
subcutaneous administration in rats. As in the previous
study, the in vivo half-life of both fusion proteins was
increasedincomparisontounfusedIFN-
a
(Table 11.2).
Both AUC and circulating half-life of IFN-
a
2b-DOM7h-14
were increased in comparison to values obtained with
HSA-IFN-
a
2b (AUC 342.5 hmg/mL and half-life of
28.3 h for IFN-
a
2b-DOM7h-14 vs. AUC 137.1 hmg/mL
and half-life of 19.7 h for HSA-IFN-
a
2b), which is in
agreement with the results from the study with animals
receiving intravenously administered IFNs described
earlier. Consistent with the improved in vivo half-life of
IFN-
a
2b-DOM7h-14 compared with HSA-IFN-
a
2b, the
AlbudAb fusion protein was also cleared at a lower rate
following subcutaneous administration (clearance rate of
5.9mL/h/kg with IFN-
a
2b-DOM7h-14 vs. 16.7mL/h/kg
for HSA-IFN-
a
2b). Bioavailability following subcutaneous
administration was also improved with IFN-
a
2b-DOM7h-14
HSA-IFN-
a
2b. When compared directly, the antiviral activ-
ity of IFN-
a
2b-DOM7h-14 is 15.8-fold greater than that of
HSA-IFN-
a
2b. On a molar basis, this is equivalent to a 5.8-
fold increase in the in vitro antiviral efficacy of IFN-
a
2b-
DOM7h-14 in comparison with HSA-IFN-
a
2b; therefore,
even in the presence of HSA, the in vitro antiviral efficacy of
IFN-
a
2b-DOM7h-14 is significantly higher than that of
HSA-IFN-
a
2b as would be expected based on the in vitro
potency of these two molecules observed in the HEK293-
Blue IFN-
a
/
b
reporter cell assay.
In summary, we have demonstrated using two distinct in
vitro assays, one of which is a measure of the desired
antiviral activity of the therapeutic, that AlbudAb technol-
ogy can be used to generate fusion proteins with superior
potency compared with genetic serum albumin fusions. This
superior potency is maintained in the presence of physio-
logically relevant concentrations of HSA; therefore, it is
possible that the improved potency of AlbudAb fusion
proteins in comparison to HSA fused molecules will also
correlate directly with improved efficacy in vivo. Compari-
son of the pharmacokinetics and in vivo efficacy is the
subject of Sections 3.2 and 3.3.
TABLE 11.1 Pharmacokinetics of Interferon Fusion
Proteins Following Intravenous Administration in Rats
IFN-
a
2b-
DOM7h-14
HSA-IFN-
a
2b
Unfused
IFN-
a
T
1/2
elim (h)
22.6
14.2
1.2
C
max
(
m
g/mL)
34.7
60.1
25.3
11.3.2 Pharmacokinetics of HSA and AlbudAb Fusion
Proteins
AUC
0-
1
737.5
689.2
18.8
Clearance (mL/h/kg)
2.7
3.1
135.2
In order to compare the in vivo half-life of IFN-
a
2b-
DOM7h-14 and HSA-IFN-
a
2b, the pharmacokinetics of
Source: Reproduced from Reference [20] by permission of Oxford Univer-
sity Press.






Search WWH ::

Custom Search