Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
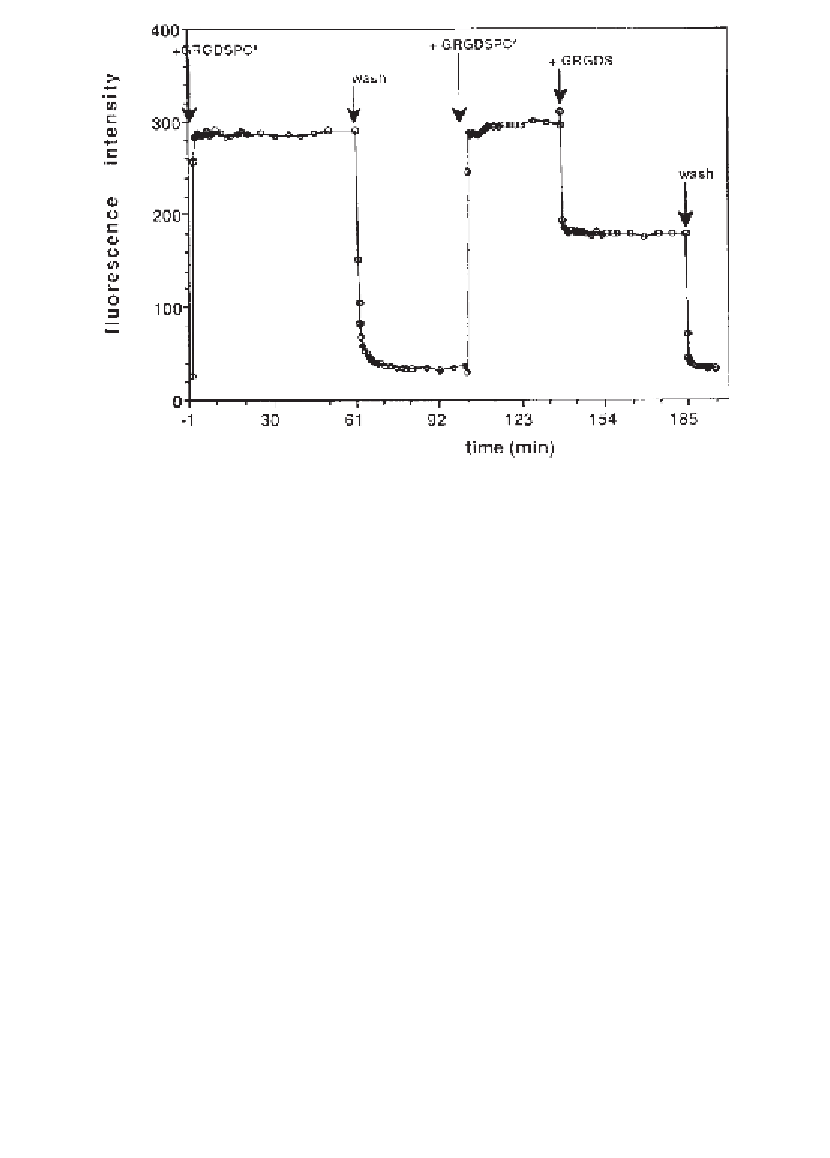
Fig. 5. Association and dissociation kinetics of peptide binding to
α
IIb
β
3 in bilay-
ers by TIRFM. Bilayers with
3 in DMPG/DMPC vesicles were formed by vesicle
fusion. TRITC-labeled peptide GRGDSPC was added at a concentration of 3300 n
M
and association kinetics were followed by measuring the time course of the fluores-
cence intensity (
α
IIb
β
) at an excitation of 514 nm. After reaching the equilibrium, the cell
was washed with Buffer C (4 mL/min) while monitoring the time-course of fluores-
cence intensity. TRITC-labeled GRGDSPC-peptide could be dissociated by addition
of a 100-fold molar excess of unlabeled GRGDS-peptide. The background signal of
about 180 relative fluorescence units was caused by labeled peptide which stayed free
in solution and could be abolished by washing with buffer.
°
2.2. Vesicle Preparation
1.
Lipid stock solution: lyophilized phospholipids DMPG and DMPC (Avanti Polar
Lipids, Alabaster, AL) were dissolved in chloroform/methanol 2:1 at a concen-
tration of about 15 m
M
. Precooled solvent (30 min at -20
°
C) is easier to pipet
(
see
Note 2
).
2. 2
M
(w/v) Tris-HCl, adjust pH to 7.4 with concentrated HCl.
3. 5
M
(w/v) NaCl, warm the solution to facilitate dissolvation.
4. Buffer A: 20 m
M
Tris-HCl pH 7.4, 50 m
M
NaCl, 1 m
M
CaCl
2
.
5. Buffer B: Dissolve 45.4
L Triton X-100 in buffer A, final volume 50 mL, final
concentration 0.1% (w/v) (
see
Note 3
).
µ
6.
About 500 mg of BIO-Beads SM-2 (Bio-Rad, Richmond, CA) were first washed
with 50 mL methanol and then with 500 mL distilled water. The wet beads were
collected on a sintered glass funnel (
see
Note 4
).
Search WWH ::

Custom Search