Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
A-1
O
OO
A-1
O
OO
O
O
O
P
O
O
P
O
O
O
-
G1
G1
OO
O
OO
O
2
5
5
+
-
-
1
1
N
2(GlcN6P)
N
2(GlcN6P)
3
2
O
2´
(A58)
O
2´
(A58)
4
6
6
N
1
(G33)
N
1
(G33)
4
3
O
4
(U43)
O
4
(U43)
N
1
(G32)
N
1
(G32)
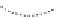
Figure 5.4 Proposed glmS ribozyme comprehensive mechanism of action through
coordinated proton transfer. The schematic diagram depicts the proposed transfer of
active site protons (numbered green circles) and their hydrogen bonding interactions
with active site functional groups (green arrows) before and after general base catalysis
initiated by GlcN6P (left and right, respectively). In this manner, G33 may be activated to
serve as the ultimate general base for deprotonation of the 2
0
hydroxyl at A-1, while
GlcN6P is concomitantly activated to serve as the general acid catalyst for protonation
of the 5
0
oxygen at G1.
both the general acid and general base would be predominant. However, the
G33A mutation has been demonstrated to completely inactivate the
glmS
ribozyme.
13-15
The
glmS
ribozyme therefore defies simple mechanistic
explanation based on independently functioning general acid and base
catalysts.
An alternative interpretation of the
glmS
ribozyme pH-reactivity profile
proposes that GlcN6P functions as the coenzyme by playing roles as both a
general base and acid catalyst (
Fig. 5.4
). In this model, the kinetic profile of
the ribozyme reflects the contributions of GlcN6P operating at its liganded
p
K
a
.
6
A number of studies have demonstrated the ability of the
glmS
ribo-
zyme to tune the catalytically critical p
K
a
of its coenzyme amine group.
Raman crystallography directly measured the p
K
a
of GlcN6P coenzyme
binding to RNA, where the p
K
a
of the amine was lowered to 7.26 and
the p
K
a
of the coenzyme phosphate was raised to 6.35 from its solution
p
K
a
of 5.98.
39
Therefore, the
glmS
ribozyme appears to aid coenzyme func-
tion by tuning the p
K
a
of the amine group to allow for optimal acid-base
catalysis.
The ribozyme thus exhibits an apparent reaction p
K
a
that simply and
precisely corresponds to the p
K
a
of the coenzyme's amine functionality.
The pH-reactivity profile gives further insight into mechanistic detail, indi-
cating that the coenzyme might be acting as both the general acid and base,
with more than one proton transfer occurring nearly simultaneously. The















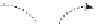



































Search WWH ::

Custom Search